AGR 301 :: Lecture 11 :: SUNFLOWER Helianthus annuus
![]()
IMPORTANCE OF SUNFLOWER OIL
- Among the vegetable oils most suitable to coronary system
- High level of linoleic acid and absence of linolenic acid
- PUFA (Polyunsaturated fatty acid) – Linoleic content is more (67%) and about 90% unsaturated (+monounsaturated 21%)
- Major ingredient in margarine and shortening products

Origin & spread
- Probably from South - West America
- Sunflower was introduced into Europe in 16th century
- Reached Europe from Mexico via Spain
- It was ornamental
- Reached Russia via Holland in 18th century
- First commercial production for oil -1830-40
Sunflower world scenario in 1999 (Million ha & million t)
Country |
Area |
Production |
Productivity |
Russian Federation |
5.94 |
6.75 |
1.14 |
Argentina |
2.19 |
3.80 |
1.73 |
Ukraine |
3.92 |
5.32 |
1.36 |
India |
2.13 |
1.12 |
0.53 |
USA |
0.71 |
0.96 |
1.36 |
Romania |
0.98 |
1.53 |
1.55 |
China |
1.03 |
1.82 |
1.77 |
World |
23.70 |
31.33 |
1.32 |
(FAOSTAT, 2006)
Indian Scenario of sunflower
State |
Area |
Production |
Productivity (kg/ha) |
Karnataka |
1427 |
787 |
552 |
Maharastra |
355 |
206 |
580 |
AP |
444 |
298 |
671 |
Punjab |
17.8 |
28.7 |
1612 |
Bihar |
22.6 |
26.4 |
1345 |
UP |
12.6 |
16.1 |
1278 |
TN |
17.1 |
21.2 |
1240 |
India |
2339.6 |
1439 |
615 |
(Ministry of Agriculture, Govt. of India, 2005-06)
Favourable features for growth of sunflower in India
- Wide adaptability
- Photoperiod insensitiveness
- Shorter duration (60-100 days)
- High quality edible oil (PUFA)
- High seed multiplication ratio (>1: 80)
- Easier & cheaper cultivation
- Remunerative market price
- Suitable for mechanization
Stages of Sunflower
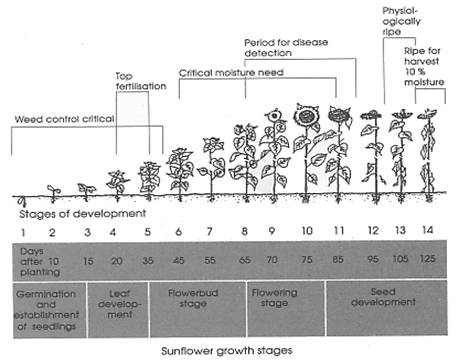
Erect, tall usually un-branched
- Plant height, head size, days to flowering & maturity are all vary due to environment
- Root – tap root - but thick root mat with short tap root is common
- May be problem in light soil to heavy mass - lodging
- Limitations in the exploitation of soil moisture & nutrients
- Earthing-up interferes with roots
- Irrigation frequency should be short to meet the demand
- Waterlogging adversely affects the crop due to weakening of anchorage and proliferation of fungal diseases
- The stem
- Mostly unbranched
- Branching is not desirable
- Basal branching may be useful
- Leaf axil branching problem
- N triggers branching
- Green stem contributes for photosynthesis
- Ht varies
- 80-120 short can accomododate more plants
- 120-150 medium
- 150-180 tall
- The leaf
- Varies with plant type and environment
- Limited to number of nodes
- 8 to as many as 70
- Arranged alternate at right angle
- The inflorescence
- Capitulum borne terminally
- Surrounded by one or more whorls of bracts called involucre (modified leaves)
- Head diameter is yield deciding factor
- Anthesis and fertilization
- Flowering from periphery
- Outermost opens first
- Daily 1-5 rows continues up to 5-10 days
- The seed
- Seed is called ‘achene’
- Seed size 7-25mm long, 4-13m long,3 -7.5mm thick
- Dormancy normally 10-45 days
- Oil content 36-37%
- 1000 seed weight 43-45g
The climate
Temp range 8-34°C
Optimum 20 & 25°C
Requires cooler (15-20°C) growing period and warmer maturing period (20-25°C)
Base minimum is 10°C
High temp (>38°C) in post-anthesis inhibit quantity and quality of oil
Rainfall of 500mm, with 300 mm it can yield
Avoid flowering coincide continuous drizzle
Soil
- Can be in wide range of soils
- Any soil with good drainage is more important
- Neutral to moderately alkaline soils
- pH ranges 6.5 to 8.0
- Complete failure in sandy soil with pH 4.6
Varieties
CO1, CO2, CO 3, CO 4
Modern, K2, K1, BSH 1
EC 68415
Hybrids have advantage than varieties
- High yield potential
- Uniform crop stand
- More self-fertile, less problem of seed set
- MSFH 1, BSH 1
Seasons
Rainfed
June-July, Kharif in North
Oct-Nov
Irrigated
- Dec - Jan
- April – May
Field preparation
- Fine tilth
- Apply FYM / Compost incorporate
- Ridges and furrows
Spacing
- 30 to 60cm according to variety
- 10 to 15 cm for short & medium stature
- 15 to 30 cm for tall (>120cm)
Seed rate
- @ 2 seeds per hole
- Seed weight of 45g/1000
- 30 x 10 30 kg
- 30 x 15 20kg
- 30 x 30 10kg
- 60 x 30 5kg
Seed treatment
- Trichderma 4 g /kg
- Azospirillum 600 g to one ha
- Soaking the seeds
- 2% ZnSO4 for 12hrs and
- Shade drying for rainfed sowing is desirable
Sowing
- Well prepared deep, friable seedbed is more preferable
- Depth of sowing 3-5cm

Plant population
- 55,000 to 98,000 /ha almost same yield
- If the head diameter is <10cm more population
- If >20cm less population
Thinning
- Highly sensitive to intra-specific competition
Nutrient management
- Fast growing high oil yielding thus requires more nutrients
- Low yield in India is attributed to poor fertile soil, cultivated in rainfed conditions
- A crop yielding 2 t seed, 3.2t stover and 0..8t root uptakes
82 kg N, 13 kg P, 60 kg K, 9.4 kg S, 37 kg Ca and 21 kg Mg.
State wise nutrient recommendation
- TN 40-20-20
- UP 80-60-40
- AP - Rainfed 60-30-0
- Irrigated Hybrids 60-90-30; Variety 30-60-30
Weed management
- Fluchloralin / Pendimethalin
- 2.0kg as pre-mergence
- High volume spray
- Hoeing and weeding on 15th day & 30th day
- Within three days irrigate the filed
Water management
- Immediately after sowing
- 4-5 days later once
- Interval of 7-8 days
- Seeding, flowering and seed development stages are critical
Seed setting and filling
- Problem is seen with poor seed setting
- This problem is more in warmer regions
- In India seed filling under good management is only 75%
- It will be as low as 10-20%
- Reasons
- Genetic
- Environmental
- Physiological
- Availability of pollinators
Maturity
Physiological maturity (30-40% seed moisture
When the back of the head turns green to lemon yellow
There will be 5-6 green leaves at this stage
Harvest maturity (10-12%)
Delay beyond harvest maturity severe yield loss


Cropping systems
Sequential cropping
- Southern India
- Rainfed - Sunflower – millets/pulses
- Irrigated- Rice – sunflower
- North
- Rainfed - SF – wheat / chickpea
- Row intercrop
- Groundnut + SF
- Pigeanpea + SF
- Castor + SF
- Pulses + SF
Multiple choice questions
- Origin of sunflower is _____
a. India b. Argentina c. South west America - Scientific name of sunflower is ______
a. Helianthus annuus b. Carthamus tinctorious c. Sesamum indicum - Total production of sunflower in the world is ____ m tonnes
a. 22.27 b. 28.48 c. 33.23 - Total production of sunflower in India is ______ m tonnes
a. 2.25 b.1.25 c.3.25 - Oil content of sunflower is _________
a. 38-40 % b. 30-32 % c. 36-37 % - Nutrient recommendation for sunflower in Tamil Nadu is ________ kg NPK/ha
a. 80:60:40 b. 60:30:0 c.40:20:20 - Saturated fatty acid content in sunflower is ________
a. 12 % b. 15 % c. 10 % - Mono unsaturated fatty acid content in sunflower is ________
a. 16 % b. 15 % c. 10 %
| Download this lecture as PDF here |
![]()