Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1. Tractor Mechanics
Module 2. Traction
Module 3. Introduction to Transmission System
Module 4. Clutch System
Module 5. Gear Box
Module 6. Differential and Final drive
Module 7. Brakes
Module 8. Steering system
Module 9. Hydraulics
Module 10. Power Transmission
Lesson 1. Determination of Centre of Gravity of wheeled and track type tractors
A tractor, in Indian context, can be defined as a wheeled, self propelled vehicle used as power source for towing agricultural implements or for driving threshers, pump sets or performing similar agricultural operations. Most Indian agricultural tractors fall in the category of general purpose tractors. For the purpose of understanding, the tractor can be divided into tractor engine and tractor system. The tractor engine on Indian agricultural tractors is the usual multi cylinder compression Ignition engine producing high torque at low speed. It is the tractor systems that make the agricultural tractor different from any other automobile designed for running on the roads.
The tractor systems include study of tractor mechanic, traction, transmission system, steering system, brakes, hydraulics and location of the controls.
Tractors mechanics present a very complex picture towards understanding of the design behind agricultural tractor. Some of the parameters that make the understanding of tractor mechanics difficult are listed as follows:-
Location of the center of gravity.
Traction produced by the traction devices.
Surface condition and slope of surface on which tractor is used.
Type of hitch system.
Load characteristics of the implement being used.
Power take off- both stationary as well as tractive.
Varied operational conditions.
Response of the tractor to dynamic forces.
Before going in to study the tractor mechanics, some assumptions that can be made to make the study less complex are listed as follows:-
Tractor is a four wheeled general purpose tractor with rear wheel drive.
The tractor has a uniform forward motion on a level surface.
The point of pull is mid way between the traction wheel and the line of pull is parallel to the direction of motion of the tractor.
The soil reaction is vertical and passing through the centre of the axle.
The traction force at the point to contact of traction wheel and ground surface is tangent to the traction wheel.
The rolling resistance is initially neglected.
All minor forces are neglected.
Location of Centre of Gravity
Importance: - The location of the centre of gravity determines the weight distribution on the wheels. Height of the centre of gravity above the ground is important especially during working on slopes or during high speed turns. Distance in front of the rear axle helps in improving pull exerted by the tractor.
In this context, it is important that the centre of gravity should be as low as possible leading to low ground clearance. But, since the tractor is supposed to move over, many times standing crop, a low ground clearance can cause a lot of problem. Distance in front of the rear axle increases the wheel base of the tractor. Longer wheel base means larger turning radius. But in the case of agricultural tractors, shortest possible turning radius is required, which is contrary to the location of the centre of gravity.
In general, it is a tendency while designing a tractor that the centre of gravity be as low as possible from stability point of view. On the other hand the tendency to have high ground clearance especially for use of tractors in growing crops, leads to the center of gravity being raised. Therefore a trade- off has to be struck to keep the center of gravity low and have high clearance over the crops, while designing the agricultural tractors.
As a thumb rule, the rear-wheel drive tractors usually have 55-80% of weight on the rear wheels. In case of all wheel drive tractors, the center of gravity is locatedahead of thecenter of the tractor. For the track type tractors, the centre of gravity is located ahead of the middle plane of the tracks so that uniform soil pressure can be obtained under normal pull and load.
Determination of location of center of gravity
For accurate analysis of the mechanics of a tractor, it is important to determine the location of the center of gravity. A tractor consists of many fixed and movable parts. The fixed parts may include various assemblies such as the engine, gearbox, radiator, front axle, rear axle etc. on the other hand the movable parts include oil in the sump, air cleaner oil, coolant in the radiator, the operator changing his position, location of center of gravity, the affect of movable components is neglected.
It is important to use the three reference planes to determine the location of center of gravity. Since the tractors are approximately symmetrical about the longitudinal vertical plane passing through the mid points of the front and rear axle, it is assumed that the center of gravity will be on this plane.
Following methods can be used to determine the location of the center of gravity:-
Suspension Method I
As shown in fig1.1(a), if a tractor is initially suspended from a point on, say the front axle using a crane hoist taking care that the front axle and rear axle are horizontal, then the center of gravity will be on the vertical plane passing.
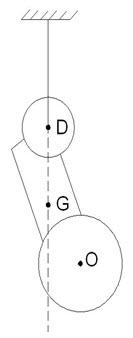
through the point of suspension. If this can be repeated using another point of suspension, another vertical plane is derived. The point of inter section of these planes is the center of gravity of the tractor.
Suspension Method II
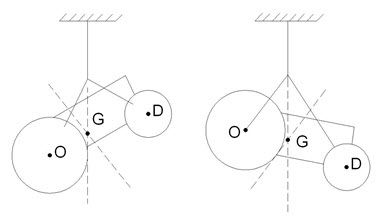
If a tractor is suspended (as shown in fig 1.2) using ropes (or chains) in such a way that one side is longer than the other. The tractor is suspended twice in such a way that one side is longer than the other. The tractor is suspended twice in such ways that in one case the longer side is attached to the rear axle and reverse in the second case. The intersection of the two vertical planes got in that case gives the location of the center of gravity of the tractor.
Balancing Method
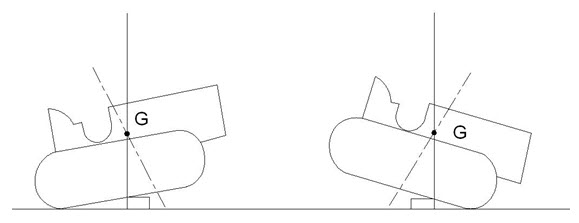
The balancing method can be used to determine the location of center of gravity of track type tractors. In this case, a large block of wood of length equal to the overall width of the tractor and height of nearly 15 cm is used as shown in fig 1.3. It is balanced on the block while driving forward and then while driving in the reverse. The two vertical planes so got give the location of the center of gravity of the track type tractor.
Weighing Method
The weighing method of finding the location of the center of gravity can be used in the laboratories. A weighing scale can be used to measure the total weight of the tractor and the reactions acting on the two wheels (fig 1.4(a) and (b)).
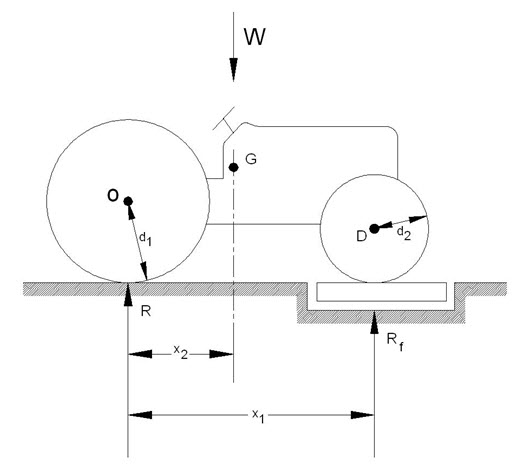
The weighing method of finding the center of gravity is easily applied. A vertical plane containing the center of gravity can be determined by the following equation:
![]()
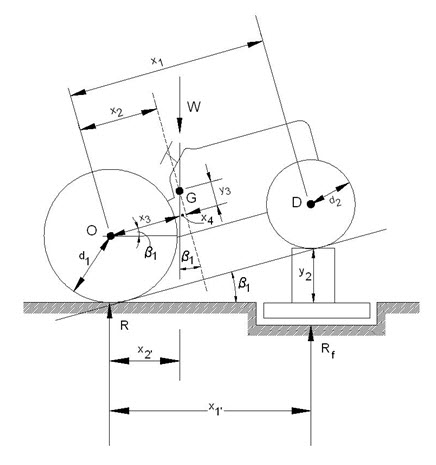
If the front wheel of the tractor are raised a distance y2 and Rf´ determined, another plane containing the center of gravity may be obtained from the same equation (fig.14.6):
![]()
The intersection of these two planes will locate the center of gravity G. This location can be satisfactorily indicated by chalking the lines of the planes on the side of the tractor.
It should be pointed out that x1´ can be determined approximately by:
![]()
The error involved in using equation 9 is small and, in fact, is justified, considering weighing errors such as the effect of the tire tread and increased deformation of the rear tire when the tractor is tipped etc.