Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1. Role of mechanization and its relationsh...
Module 2. Performance and power analysis
Module 3. Cost analysis of machinery- fixed cost a...
Module 4. Selection of optimum machinery and repla...
Module 5. Break-even point and its analysis, relia...
Module 6. Mechanization planning
Module 7. Case studies and agricultural mechanizat...
Topic 8
Topic 9
Topic 10
Lesson 7. Importance of farm machinery management
The importance of farm machinery management has increased in modern farming operations because of its direct relation to the success of management in combining land, labour and capital for a satisfactory profit. Many problems of machinery management are encountered such as:
a) How many equipment should be owned?
b) What size of equipment is required?
c) How often should the machinery be traded?
d) Should a custom operator be hired or a machine be leased?
e) How can the rapidly increasing fuel costs be kept to the minimum?
Following are some of the suggestions to help a farmer to prepare himself to satisfy the increasing needs for machinery management:
(i) Learn how to use the machinery principles.
(ii) Keep complete records of fieldwork done by various machines and the number of working days available for critical field operations. By knowing average capacity of machines and number of workdays available, a more effective job of selecting machinery is possible.
(iii) Know how to accurately estimate costs for any machine and how to combine costs of machines to estimate total cost for an entire systems. Many important decisions are based on costs.
(iv) Know how to improve equipment reliability. Always work towards the elimination of unnecessary down time.
(v) Improve field efficiencies with machines to cut costs and complete more work in the available time.
(vi) Develop a lone-range plan for your farming operations.
(vii) Keep thinking of ways to improve the efficient ownership and management of agricultural machinery.
(viii) Review the problems encountered.
Measures of performance of farm equipment are the rate and quality with which the operations are accomplished. This is generally expressed in terms of capacity as well as efficiency.
Capacity: Calculations of machine capacity involve measuring of area covered, weight of material and time. The machine capacity is normally expressed in three ways:
a) Field capacity
b) Material capacity
c) Throughput capacity
Field capacity: It is the rate of field coverage. It is also expressed in two ways:
a) Theoretical field capacity
b) Effective field capacity
Theoretical field capacity: It is the rate of field coverage if the machine is performing its functions 100% of the time at its rated speed while covering 100% of its rated width.
Theoretical field capacity (Ct) is expressed as

Where,
S = average speed of machine, mph
w = rated width of machine, ft
Or,

Where,
S = average speed of machine, km/h
w = rated width of machine, m
Thus, these values represent the best that a machine can do if there were no stoppages and the machine was taking its full width all the time.
Effective field capacity: The farm equipment seldom covers its rated width and performs its function 100% of the time. Therefore, it never meets the theoretical field capacity. Effective field capacity is the actual rate of field coverage. It is expressed as
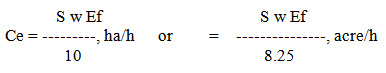
Where,
Ce = effective field capacity, ha/h
Ef = field efficiency, fraction