Module 7. Flow through orifices, mouthpieces, notches and weirs
Lesson 19
ORIFICES, VENA CONTRACTA, HYDRAULIC COEFFICIENTS
19.1 Introduction
In engineering, in particular fluid dynamics and hydrometry, the volumetric flow rate, (also known as volume flow rate, rate of fluid flow or volume velocity) is the volume of fluid which passes through a given surface per unit time. The SI unit is m3/s (cubic meters per second). It is usually represented by the symbol Q. Flow rate can be measured by orifice, notches, weirs etc. which will be discussed in this module.
19.2 Orifice
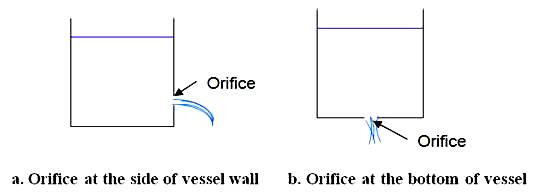
Fig. 19.1 Orifice
An orifice is an opening in the side or bottom of a vessel/tank to measure the discharge. Fig. 19.1 shows an orifice.
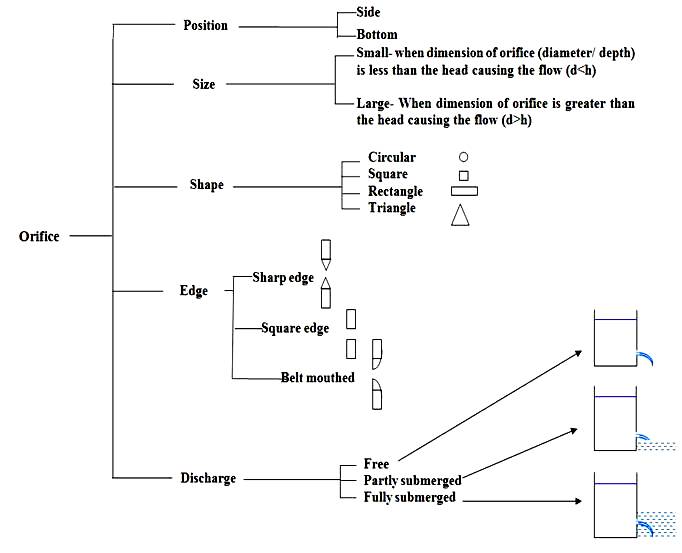
Fig.
19.2 Classification of orifice
19.3 Vena Contracta
Suppose a circular sharp edged orifice is in side of tank which discharges liquid directly into atmosphere (Fig. 19.3). Water jet from the orifice converges to minimum cross-section at XX’ and then diverges again. The section at which the cross-sections area of jet is minimum & less than that of orifice is known as Vena Contracta.
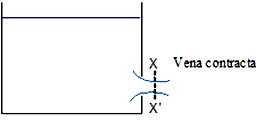
Fig. 19.3 Minimum cross section at XX’ is known as vena contracta
19.4 Flow Velocity at Vena Contracta
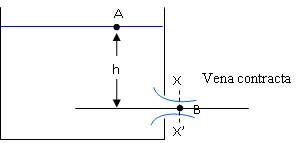
Fig 19.4 Vena contracta
At point A At point B
pA = 0 pB = 0
VA = 0 VB = VB
ZA = h ZB = 0
From Bernoulli’s theorem:
![]()
Placing values at points A and B
![]()
![]()
Above equation is known as Torricelli’s theorem.
19.5 Hydraulic Coefficient
1. Coefficient of velocity Cv
2. Coefficient of contraction Cc
3. Coefficient of discharge Cd
4. Coefficient of resistance Cr
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Actual velocity < theoretical velocity.
So, value of all coefficients < 1.
![]()