Module 7. Flow through orifices, mouthpieces, notches and weirs
Lesson 22
TYPES OF NOTCHES, RECTANGULAR AND TRIANGULAR NOTCHES, RECTANGULAR WEIRS
22.1 Flow Over Notches and Weirs
22.1.1 Notch
A notch may be defined as an obstruction over which the flow of liquid occurs. As the depth of flow above the base of the notch is related to the discharge, the notch forms a useful measuring device. In case of measuring tank or reservoir, the opening is provided at the side of the tank such that the liquid surface in the tank is below the top edge of the opening. In fact, this is a large opening which has no upper edge, so that it has a variable area depending upon the level of the free surface.
22.1.2 Weir
A weir is a notch on a large scale used for measuring the flow of a river, canal etc. It is a concrete or masonry structure of substantial breadth built across the river in the direction of flow. This allows the excess water to flow over its entire length to the downstream side. Thus a weir is similar to a small dam constructed across the river, with a difference that the excess water flows downstream only through a small portion called spillway and in case of weir, the excess water flows over its entire length.
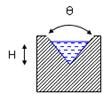
22.1.3 Nappe and crest
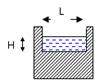
The sheet of water flowing through a notch or over a weir is known as nappe or vein. The bottom edge of the notch or the top of a weir over which water flows is known as sill or crest. The height above the bottom of the tank or channel is known as crest height.

Fig. 22.1 Nappe and crest
Table 22.1 Difference between
orifice and notch
|
Orifice |
Notch |
|
An orifice may be defined as an opening provided in the side or bottom of tank or vessel such that the liquid flows through the entire orifice.
|
A notch may be defined as an opening provided in the side of tank or vessel such that the liquid surface in tank is below the top edge of opening.
|
Table 22.2 Difference
between notches and weirs
|
Notch |
Weir |
|
A notch may be defined as an opening provided in the side of tank or vessel such that the liquid surface in tank is below the top edge of opening.
|
A weir may be defined as any regular obstruction in open stream over which the flow takes place.
|
|
Small structure |
Large structure |
|
Made of metallic plates. |
Made of concrete/bricks. |
|
Measure small flow rate. |
Measure large flow rate. |
Table 22.3 Types of notches
|
|
Types of notches |
Diagram |
Discharge/flow rate |
|
a. |
Rectangular
|
|
|
|
b. |
Triangular
|
|
|
|
c. |
Trapezoidal
|
|
Q = Q1 + Q2
|
|
d. |
Stepped
|
|
Q = Q1 + Q2 + Q3 |
22.2 Types of Weir
1. Shape
· Rectangular
· Triangular
· Trapezoidal
Table 22.4 Types of weir on
basis of shape
|
|
Types of weir |
Diagram |
Discharge/flow rate |
|
a. |
Rectangular
|
|
|
|
b. |
Triangular
|
|
|
|
c. |
Trapezoidal
|
|
Q
= Q1 + Q2
|
Note: The discharge equation for rectangular, triangular and trapezoidal weir is same as of notch.
2. Nature of discharge
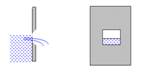
· Free: Liquid level on the downstream side is lower than the crest.
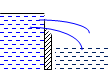
![]()
![]()
Fig. 22.2 Free flowing weir
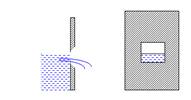
· Drowned: Liquid level submerges the crest

Fig. 22.3 Drowned weir
3. Width of crest
· Sharp: The crest is narrow

Fig. 22.4 Sharp crest weir
· Broad: The crest is broad
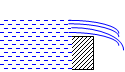
Fig. 22.5 Broad crest weir