Module 3. Pressure measuring devices
Lesson 8
MECHANICAL GAUGES
8.1 Introduction
- Manometers are suitable for
lower pressure i.e. near to atmosphere pressures.
- For measuring medium and high pressure
elastic pressure gauge such as tubes, diaphragms, bellows etc. are used.
- Elastic deformation in these
elements shows the effect of pressure.
- Since, there elements deform
within elastic limit therefore these gauges are also called elastic
gauges.
- Mechanical gauges are called secondary instruments because they
have to be calibrated with help of primary instrument such as manometer.
8.2 Simple Mercury Barometer
· Measures the absolute atmospheric pressure
· Pressure is given as p = ρgh where ρ = density of mercury, g = 9.81 m/s2, h = height of mercury in the barometer.
· Major disadvantage: fragile, mercury is harmful and may spill.
Simple mercury barometer and the photograph showing the coloumn of mercury rise in the barometer are shown in Fig. 8.1 and 8.2 respectively.
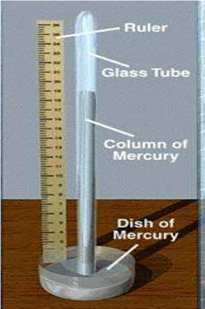
Fig. 8.2 Photograph of simple mercury barometer
8.3 Aneroid barometer
Aneroid barometer uses elastic diaphragm to measure atmospheric pressure.
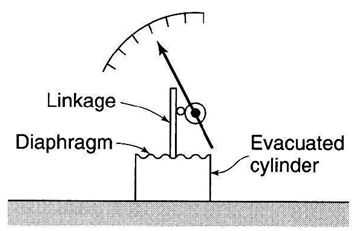
Fig. 8.3 Working principle of Aneroid barometer

Fig. 8.4 Aneroid barometer
8.4 Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauges
· It is used to measure high as well as low pressure.
· Pressure element consists of a metal tube of elliptical cross section.
· This tube is bend in a form of segment of circle and responds by bending inward due to increase in pressure
· When one end of tube is connected to source of pressure, the pressure inside the Bourdon tube causes the tube to expand and bend inward.
· A simple pinion and sector arrangement is provided to convert the linear movement of the tube into angular movement of the pointer.
· The pressure is indicated by the pointer over dial which can be graduated on a suitable scale.

Fig. 8.5 Bourdon tube pressure gauge


Fig. 8.6 Bourdon tube pressure gauge
8.5 Diaphragm Gauge
· Consists of metallic disc or diaphragm for actuating the pointer.
· When pressure is applied on lower side of diaphragm, it gets deflected upward.
· The movement of diaphragm is transmitted to a strain gauge or transducer which converts the pressure signal into electrical signal. In analogue devices, a rack and pinion system is provided which moves the pointer.
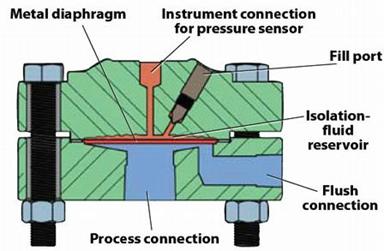
Fig. 8.7 Diaphragm gauge
8.6 Vacuum gauge
(a) Bourdon gauge can be used to measure vacuum by bending the tube inward instead of outward pressure in pressure gauge.
(b)Vacuum gauge is graduated in mm of Hg below atmospheric pressure.
8.7 Pressure Transducers
Transducers are instruments which convert one form of signal into another form of signal. Electronic pressure transducers sense the signals and convert into electronic/electrical signals which can be further processed. Few of them are strain gauge, piezoelectric, capacitive, magnetic etc.