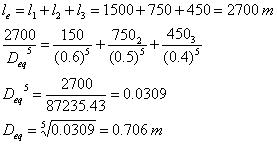Module 6. Flow through pipes
Lesson 18
DETERMINATION OF PIPE DIAMETER, DETERMINATION OF DISCHARGE, FRICTION FACTOR, CRITICAL VELOCITY
18.1 Piping Systems
a.
Pipes connected in series
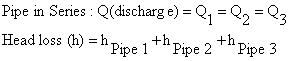
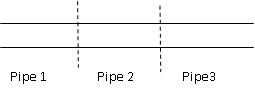
Fig. 18.1 Pipes connected in series
b. Pipes connected in Parallel
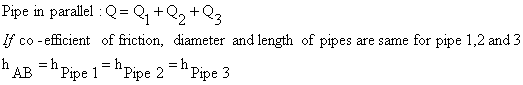
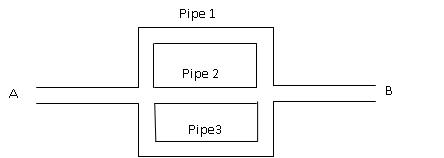
Fig. 18.2 Pipes connected in parallel
18.2
Dupit’s Equation for Equivalent Pipe
Equivalent pipe
If several pipes of different lengths and diameter are connected in series, it can be replaced by single pipe called as equivalent pipe. This equivalent pipe of same diameter will have the same loss head and discharge which several pipes connected in series will have.
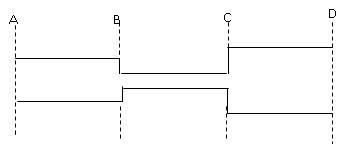
Fig. 18.3 Pipes of different lengths and diameters
connected in series
Equivalent diameter
The uniform diameter of the equivalent pipe is the equivalent diameter series or compound pipe.
![]()
Fig. 18.4 Equivalent pipe
Equivalent length
The length of equivalent pipe which has the same head loss & discharge that of series or compound pipe.
Assumption for analysis
Neglect the minor
losses (frictional loss) and consider only the major head losses (friction
loss) since hminor << hmajor

![]() ………
(iv)
………
(iv)
On
equating (iii) & (iv):
![]()
![]() ……… (v)
……… (v)
Eq. (v) is known as
Dupit’s eq. for equivalent pipe.
Case1. Sometimes length of equivalent pipe is taken to be equal to the length of compound pipe i.e.
Le = L1+ L2+ L3+ L4+……….
In such cases diameter of equivalent pipe Deq, can be calculated from Dupit’s equation.
Case2. Sometimes value of equivalent diameter is given & length of equivalent pipe requires replace compound pipe has to be determined by Dupit’s equation.
18.3 Numericals
Q 1. Three pipes are connected in series
|
Pipe |
Length (m) |
Diameter (cm) |
|
l1 |
1000 |
50 |
|
l2 |
750 |
40 |
|
l3 |
500 |
30 |
(a) Calculate equivalent diameter considering the length equivalent pipe to be equal in that of compound pipe.
(b) Determine the length of equivalent pipe for an equivalent diameter of 40 cm.
Solution
(a)
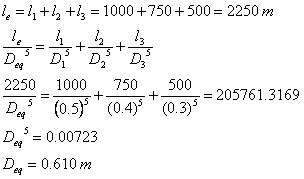
(b)
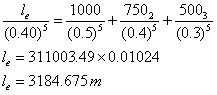
Q 2. Consider pipe 1, 2, 3 connected in series of length l1, l2, l3 respectively. D1, D2, D3 with a diameter of pipe 1, 2, 3.
|
Pipe |
Length (m) |
Diameter (cm) |
|
l1 |
1500 |
60 |
|
l2 |
750 |
50 |
|
l3 |
450 |
40 |
(a) Determine the eq. length for an eq. diameter of 50 cm.
(b) Determine the eq. diameter if the length of eq. pipe is equal to the length of compound pipe.
Solution
(a)
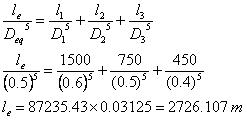
(b)