Module 7. Performance of I.C. engine
Lesson 18
NUMERICAL PROBLEMS
18.1 Numerical Problems
18.1.1 Following observations were recorded during a test on a single cylinder 4- stroke oil engine
Bore =300mm; Stroke = 450mm; Speed =300rpm; imep = 6bar; Net brake load = 1.5 kN; Brake drum diameter = 1.8m; Brake rope diameter = 2 cm.
Calculate: (i) Indicated Power
(ii) Brake Power
(iii) Mechanical Efficiency
Solution
![]()
![]() (Ans)
(Ans)
![]()
(Ans)
![]()
![]()
18.1.2 The following data refers to a petrol engine working on OTTO four stroke cycle.
Brake Power = 14.7 kW
Suction Pressure = 0.9 bar
Mech. Efficiency = 80%
Compression Ratio = 5
Index of Compression curve = 1.35
Index of expansion curve = 1.3
Maximum Explosion pressure = 24 bar
Engine Speed = 1000 r.p.m
Ratio of stroke to bore = 1.5
Find the diameter and stroke of piston.
Solution
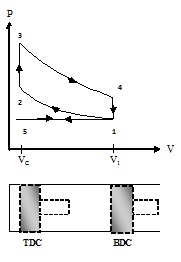
Fig. 18.1 ‘OTTO-Four stroke cycle’
Considering compression process 1-2
![]()
Or ![]()
Considering expansion process 3-4
![]()
![]()
Now work done per cycle by engine
= Work done by engine during expansion process- Work done on engine during compression process
=Area 1-2-3-4
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting V4 = 5V3 (As Compression radio, r = 5)
Net work done/cycle = 20.98 × 105V3 Nm
Therefore, mean effective pressure
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Now,![]()
Also,![]()
![]()
= 18.37 kW
![]()
Or D3 = 0.003567
Or D = 0.1527 m (Ans)
Or 152.7 mm
L = 1.5D = 229.2mm (Ans)
18.1.3 A four cylinder two stroke cycle petrol engine develops 30 KW at 2500rpm. The mean effective pressure on each piston is 8 bars and mechanical efficiency is 80%. Calculate the diameter and stroke of each cylinder with stroke bore ratio 1.5. Also calculate the fuel consumption of the engine, if brake thermal efficiency is 28%. The calorific value of fuel is 43900 kJ/ kg.
Sol:
![]()
![]()
Also![]()
Or
![]()
Or D = .062 m or 62 mm (Ans)
![]()
(ii) Fuel Consumption:
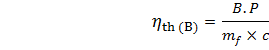
![]()
![]()
![]()
18.1.4 Following data refers to a four-stroke, four cylinder petrol engine:
Fuel Used = 19.2 kg/hour
Fuel to Air Ratio = 1:16 by weight
Suction Pressure = 1bar
Suction Temperature = 30oC
Stroke to bore ratio = 1.25
Engine RPM = 2400
Volumetric Efficiency = 78%
Find the stroke and bore of engine cylinders.
Sol: Mass of air supplied per hour = 16 × Mass of fuel supplied per hour
= 16 × 19.2
= 307.2 kg/hour
Mass of air supplied
per
second
![]()
Mass of air fuel mixture
![]()
Assuming air fuel
mixture as pure air for calculating its volume
![]()
![]()
= 0.0788 m3/s
Theoretical volume of air fuel mixture sucked by engine
![]()
![]() ………
(i)
………
(i)
This theoretical volume sucked
should be equal to stroke volume of the engine i.e.
![]()
![]()
![]()
=
157 D3 ………
(ii)
From (i) & (ii) 157 D3 = 0.101
![]()
=
0.86 m = 86mm (Ans)
![]()
18.1.5 A 4- cylinder, 4-stroke petrol engine having 90 mm bore and 130mm stroke develops 30 kW of power while running at 1500 r.p.m and using a 20% rich mixture. The theoretical air-fuel ratio is 15:1. Calorific value of petrol is 46000 kJ/ kg. Volumetric efficiency measured at 15oC and 760 mm of mercury as standard temperature and pressure is 70% and mechanical efficiency is 90%.
Find:
(i) Indicated Thermal efficiency
(ii) Brake mean effective pressure
(iii) Brake Thermal efficiency
Sol:
Total swept volume of the engine
![]()
![]()
![]() Volume
of air drawn in the engine in the suction stroke
Volume
of air drawn in the engine in the suction stroke
![]()
![]()
![]()
Volume flow rate of the 4-stroke engine
![]()
![]()
= 1.737 m3/min
This volume flow rate is at pressure 760 mm of mercury (1.013 bar) and temperature 15o C (298K).
So mass flow rate of air
![]()
= 2.057 kg/min
Mass flow rate
of fuel used = ![]()
![]()
Using 20% rich mixture actual mass flow rate of fuel used
![]()
= 0.164 kg/min
![]()
Given that, Brake power, B.P = 30 kW
![]()
![]()
![]()
(a) Indicated Thermal Efficiency
![]()
= 0.264 or 26.4% (Ans)
(b)
Brake
thermal efficiency
![]()
(Ans)
(c) Brake mean Effective Pressure
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
18.2 Unsolved Problems
18.2.1 A 4-cylinder petrol engine works on a mean effective pressure of 5 bar and engine speed of 1250 r.p.m. Find the indicated power developed by the engine if the bore is 100 mm, and stroke 150 mm.
[Ans. 6.11 kW]
18.2.2 A 4-cylinder, four stroke diesel engine runs at 1000 r.p.m. The bore and stroke of each cylinder are 100 mm and 160 mm respectively. The cut off is 6.62% of the stroke. Assuming that the initial condition of air inside the cylinder is 1 bar and 200 C, mechanical efficiency of 75% ; Calculate the air-standard efficiency and brake power developed by the engine.
Also, calculate the brake specific fuel consumption if the air/fuel ratio is 20: 1. Take R for air as 0.287 kJ/kg K and clearance volume as 0.000084 m3.
[Ans. 61.4%, 21.75kW, 0.4396 kg/kW]
18.2.3 A four stroke gas engine develops 4.2 kW at 180 r.p.m. and at full load. Assuming the following data, calculate the relative efficiency based on indicated power and air-fuel ratio used. Volumetric efficiency= 87 %, mechanical efficiency =74%, clearance volume = 2100 cm3, swept volume = 9000 cm3, fuel consumption = 5 m3/h, calorific value of fuel = 16750 kJ/m3.
[Ans. 50.2%, 7.456:1]
18.2.4 The following observations were recorded during a trial of a four stroke engine with rope brake dynamometer:
Engine speed = 650 r.p.m., diameter of brake drum = 600 mm, diameter of rope = 50 mm, dead load on the brake drum = 32 kg, spring balance reading = 4.75 kg.
Calculate the brake power.
[Ans. 5.9 kW]
18.2.5 During a 60 minutes trial of a single cylinder four stroke engine the following observations were recorded:
Bore = 0.3 m, stroke = 0.45 m, fuel consumption = 11.4 kg, calorific value of fuel = 42000 kJ/kg, brake mean effective pressure = 6.0 bar, net load on brakes = 1500 N, r.p.m. = 300, brake drum diameter = 1.8 m, brake rope diameter = 20 mm, quantity of jacket cooling water 600 kg, temperature rise of jacket water =550C, quantity of air as measured = 250 kg, exhaust gas temperature = 4200C, cp for exhaust gases = 1 kJ/kg K, ambient temperature = 200C.
Calculate: (i) Indicated power; (ii) Brake power;
(iii) Mechanical efficiency (iv) Indicated thermal efficiency.
Draw up a heat balance sheet on minute basis.
[Ans. (i) 47.7 kW; (ii) 42.9 kW; (iii) 89.9%, (iv) 35.86%]
18.2.6 A two-cylinder four stroke gas engine has a bore of 380 mm and a stroke of 585 mm. At 240 r.p.m. the torque developed is 5.16 kN-m.
Calculate: (i) Brake power
(ii) Mean piston speed in m/s
(iii) Brake mean- effective pressure.
[Ans. (i) 129.8 kW; (ii) 4.68 m/s; (iii) 4.89 bar]
18.2.7 A 4-cylinder, four-stroke diesel engine has a bore of 212 mm and a stroke of 292 mm. At full load at 720 r.p.m., the b.m.e.p. is 5.93 bars and the specific fuel consumption is 0.226 kg/kWh. The air/fuel ratio as determined by exhaust gas analysis is 25: 1. Calculate the brake thermal efficiency and volumetric efficiency of the engine.
Atmospheric conditions are 1.01 bar and 150C and calorific value for the fuel may be taken as 44200 kJ/kg.
[Ans. 36%; 76.5%]
18.2.8 During the trial (60 minutes) on a single cylinder oil engine having cylinder diameter 300 mm, stroke 450 mm and working on the four stroke cycle, the following observations were made :
Total fuel used = 9.6 liters, calorific value of fuel = 45000 kJ/kg, total number of revolutions = 12624, gross indicated mean effective pressure = 7.24 bar, pumping i.m.e.p. = 0.34 bar, net load on the brake = 3150 N, diameter of brake wheel drum = 1.78 m, diameter of rope = 40 mm, cooling water circulated = 545 liters, cooling water temperature rise = 250 C, specific gravity of oil = 0.8.
Determine: (i) Indicated power. (ii) Brake power. (iii) Mechanical efficiency.
Draw up the heat balance sheet on minute basis.
[Ans.
(i) 77 kW; (ii) 61.77 kW; (iii) 80.22%]