Module 2. Information systems
Lesson 3
TYPES OF INFORMATION SYSTEMS
3.1 Introduction
This lesson introduces different types of information systems being used in business organization for efficient operations and management. These topics will be useful for students to familiarize themselves with different kinds of information systems and their objectives and functioning.
The discipline of information system is still in evolutionary phase. Previous chapter had discussed the growth and expansion of information systems since usage of computers in business data processing. Over the years, needs of management and role of end users increased in business operations to compete at global level and accordingly more sophisticated information systems emerged to meet users’ requirements. Conceptually, applications of information systems that have been developed to support business activities can be classified in many different ways. However, these information systems can be broadly categorized into two categories as follows on the basis of their roles in operations and management of a business.
· Operations Support Systems
· Management Support Systems
In addition to above categories, several other information systems provide support in both operations as well as management of the business. Some information system may be categorized under general support systems, for example, business expert systems, functional business system and strategic information systems. Fig. 3.1 depicts the categories of the various information systems based on their role in operations and managerial decision making.
3.1.1 Operations support systems
Data is generated as by-product of transactions or when an event takes place in an organization. For example, each transaction generate some data in events such as receipt of milk at dock yard, distribution of milk to different sections for product manufacturing, handling losses during manufacturing process, quality control of milk products etc. This data is recorded, processed and used to carry out routine business operations. Information systems which use such kind of data are called operations support systems. These systems produce a variety of information products for internal and external use. However, such systems do not emphasize on producing specific information products that can be used by managers. In order to make use of such products further processing of the output is usually required. Such processing is done by management information systems. Role of operations support systems is to efficiently process business transactions of routine nature (such systems are called as Transaction processing system (TPS)), control industrial processes, support organizational communication and update databases.
3.1.2 Management support systems
These systems provide information and decision support for effective decision making by managers. There are various types of information systems such as MIS, DSS and EIS that support a variety of decision making process at different managerial level in an organization.
3.1.3 General support systems
General support system includes various information systems such as strategic information system (SIS) which provides support to business organization to gain strategic advantage over its competitors, functional business systems (FBS) which focus on operational and managerial applications in support of basic business functions such as accounting, inventory, marketing, production etc., business expert systems (BES) that provides expert advice on specific complex problems and acts as an expert in specific problem area.
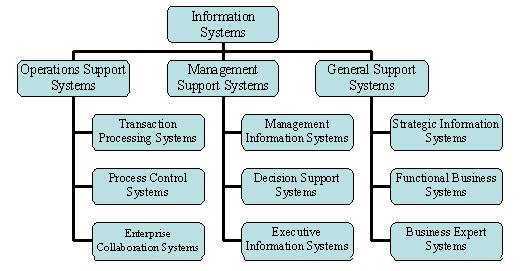
Fig. 3.1 Classification of information systems based on their role in business
3.2 Management Information Systems (MIS)
There is no consensus on definition of the term MIS. A number of terminologies are being used for MIS such as “information processing system”, “information and decision system”, “organizational information system”, or simply “information system” to refer to the computer based information system. However MIS in general can defined as “An integrated user-machine system for providing information to support operations, management, and decision making functions in an organization. The system utilizes computer hardware and software; manual procedures; models for analysis, planning, control and decision making; and a database”.
An integrated system does not mean that MIS is a single, monolithic structure rather it means that various components of information system fit into an overall design. MIS is a broad concept rather than a single system. MIS enhances job performance throughout an organization. At highest management levels, it provides information to help management to make strategic decisions. At other levels, MIS provides the means through which organizational activities are monitored and information is distributed to management, employees, and customers. An effective MIS ensures to meet appropriate presentation formats and time frames required by operations and senior management. A schematic diagram of MIS is shown in fig. 3.2 given below.
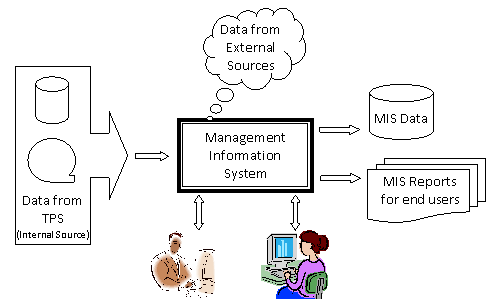
Fig 3.2 Conceptual frame work of MIS
MIS are designed to achieve the following goals:
· Enhance communication among employees.
· Deliver complex material throughout the institution.
· Provide an objective system for recording and aggregating data.
· Reduce expenses related to labor-intensive manual activities.
· Support the organization's information needs.
MIS should have a clearly defined framework of guidelines, policies, practices, standards, and procedures for the organization. These should be followed throughout the organization in development, maintenance, and use of MIS. It should be supportive of the institution's longer term strategic goals and objectives. On other extreme, it is also used for routine transaction processing to ensure basic control is maintained over day to day activities.
3.3 MIS versus Data Processing
Some significant distinguishable points between MIS and data processing as highlighted in table 3.1 as given below:
Table 3.1 MIS versus Data processing
|
Data Processing |
MIS |
|
This term was used prior to 1970s |
This concept started in late 1960s and became popular in 1970s |
|
Information is considered as by product of data processing activities |
Information is considered as valuable resource for general purpose support to business operations |
|
Primarily designed for transaction processing and record keeping with the aim to reduce cost of routine data processing activities in accounting areas |
Focus on developing business applications that provided managerial end users with predefined management reports that would give managers the requisite information for decision making |
|
Represents automation of fundamental operations, routine processing to support operations |
MIS is more comprehensive, it encompasses processing of wider range of organizational functions and management processes |
|
Process raw data generated through internal or external transactions |
Generally process the information produced from data processing system |
|
Output results in form of updated databases, bulky reports using simple and straight forward computations for line workers |
Output reports in abstract form in pre- specified format for managers for decision making. |
|
Independent approach for data processing for various applications |
Integrated approach for processing data to meet the organizational information needs. |
3.4 Decision Support System
To run an organization manager need to take decisions which require information from different sources. The more information you have, based on experiences or from internal/ external sources, the better your decisions will be. For making quality decisions managers need best available tools to help them. Before reaching to any conclusion managers should do following to the best of their abilities:
· Thoroughly check wide range of alternatives
· Weigh costs and risks of both positive and negative consequences
· Intensively search for new information for evaluating alternatives
· Take all new information into account, even when it doesn't support initial course of action
· Re-examine positive and negative consequences of all alternatives, including initially rejected ones
· Make detailed provisions for implementation, including contingency plans for known risks
A decision is a choice between alternatives based on estimates of the values of those alternatives. There are many approaches to decision-making since there exists wide range of domains in which decisions are made therefore concept of decision support system is very broad. In general, DSS is usually referred to computer based information system that performs a supporting role in decision making process. Computerized DSS became feasible during mid-1960s with the development of minicomputers, timesharing operating systems and distributed computing. DSS help managers to make better decisions by combining massive amounts of historical and current data from internal information systems and external sources with sophisticated analytical models and tools.
DSS may be defined as "an interactive, flexible, and adaptable computer-based information system, especially developed for supporting solution of a non-structured management problem for improved decision making. It utilizes communication technologies, specialized databases, knowledge and/ or analytical models, computer based interactive interface that allows a decision maker to apply his/her own insights and judgment for making unstructured or semi structured business decisions".
DSS provides interactive ad-hoc support to assist managers during decision making process. DSS tends to be used in planning, analyzing alternatives, and trial and error search for solutions. DSS incorporate variety of decision models and are thus capable of performing what-if analysis. DSS differ from traditional IS because each DSS is tailored to a specific managerial task or special problem, its use is limited to that task or problem. DSS tend to be designed to serve management control level and strategic planning level managers. These systems produce information by taking output of TPS and MIS as input data and other inputs may also be collected or generated from external environment. Since strategic information is less structured in comparison to tactical information, therefore, it is difficult to develop DSS. An MIS uses internal data to supply useful information. A DSS uses internal data as well as external data to help analyze various decision making problems. Analyzing complex problems with interactive decisions is the primary reason for an organization to use a DSS. For example a production manager in a dairy plant may use DSS to perform what-if analysis to decide how much product should be manufactured based on expected demand in future, location and availability of raw material required to manufacture the product, risk analysis etc.
3.5 DSS versus MIS
Characteristics of MIS and DSS are compared as given below in table 3.2:
Table 3.2 Comparison of MIS and DSS
|
MIS |
DSS |
|
Structured decisions |
Semi-structured, unstructured decisions |
|
Reports based on routine flow of data |
Focused on specific decisions / classes of decisions |
|
General control of organization |
End-user control of data, tools, and sessions |
|
Structured information flows |
Emphasizes change, flexibility, quick responses |
|
Presentation in form of reports
|
Presentation in form of graphics, Greater emphasis on models, assumptions, and ad hoc queries |
|
Traditional systems development |
Develop through prototyping; iterative process |
3.6 Types of Decision Support Systems
· Data-driven DSS: Data-Driven DSS extracts useful information from massive amount of data taken from company's TPS and MIS for taking decisions by executives. Data-Driven DSS emphasizes on manipulation of large databases of structured data and especially a time-series data of organization and sometimes external data. Simple file systems accessed by query and retrieval tools provide the most elementary level of functionality. Data warehouse systems that allow the manipulation of data by computerized tools tailored to a specific task setting provide additional functionality. Data-Driven DSS with Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) provide the highest level of functionality and decision support that is linked to analysis of large collections of historical data.
· Model-driven DSS: Model-Driven DSS includes systems that use accounting, financial, representational, optimization, statistical, or simulation models. Model-Driven DSS emphasizes on access and manipulation of data using models. Simple statistical and analytical tools provide the most elementary level of functionality. Model-Driven DSS use data and parameters provided by decision-makers to aid them in analyzing a situation. Such DSS are not data intensive therefore do not require large databases. These systems are separated from main Information Systems of an organization and primarily used for typical "what-if" analysis. That is, "What will be effect on profit, if we increase production of products and decrease the shipment time?" These systems rely heavily on models to help executives to assess the impact of their decisions on the organization, its suppliers, and its customers.
· Knowledge-driven DSS: Knowledge-Driven DSS can suggest or recommend actions to managers. This concept is still evolving. These are computer systems with specialized problem-solving expertise stored as facts, rules, procedures, or in similar structures. The "expertise" consists of knowledge about a particular domain, understanding of problems within that domain, and "skill" at solving some of these problems. A related concept is Data Mining. It refers to a class of analytical applications that search for hidden patterns in a database. Data mining is a process of sifting through large amounts of data to produce data content relationships.
· Document-driven DSS: Document-Driven DSS is evolving to help managers to retrieve and manage unstructured documents and Web pages. A Document-Driven DSS integrates a variety of storage and processing technologies to provide document retrieval and analysis. WWW provides access to large document databases including hypertext documents, images, sounds and video. A document-driven DSS may access documents related to policies and procedures, product specifications, catalogs, and corporate historical documents, including minutes of meetings, corporate records, and important correspondence. A search engine is a powerful decision aiding tool associated with a Document-Driven DSS.
· Communications-driven and group DSS: Communications-driven DSS includes communication, collaboration and decision support technologies for making decisions. Group DSS is a hybrid decision support system that emphasizes on the usage of both communications and decision models. Group DSS is an interactive computer-based system intended to facilitate solution of problems by decision-makers working together as a group. Group DSS supports electronic communication, scheduling, document sharing, and other group productivity and decision support enhancing activities. A number of modern technologies that are used to facilitate communication in group DSS are two-way interactive video, white boards, bulletin boards, E-mail etc.
3.7 Components of DSS
Traditionally, a decision support system has the following major components:
· The user interface
· The database
· The models and analytical tools and
· The DSS architecture and network
Data-Driven, Document-Driven and Knowledge-Driven DSS need specialized database components. A Model-Driven DSS may use simple flat-file database with few records, but the model component is very important. Experience and some empirical evidence indicate that design and implementation issues vary for Data-Driven, Document-Driven, Model-Driven and Knowledge-Driven DSS. Mathematical and analytical models are major components of a Model-Driven DSS. Each model-driven DSS has specific purpose and hence different models are needed and used. Choosing an appropriate model is a key design issue. In model-driven DSS values of key variables or parameters are changed, often repeatedly, to reflect potential changes in supply, production, the economy, sales, the marketplace, costs, and/or other environmental and internal factors. Information from models is then analyzed and evaluated by decision-maker. Concept of DSS with various components is depicted in fig. 3.3.
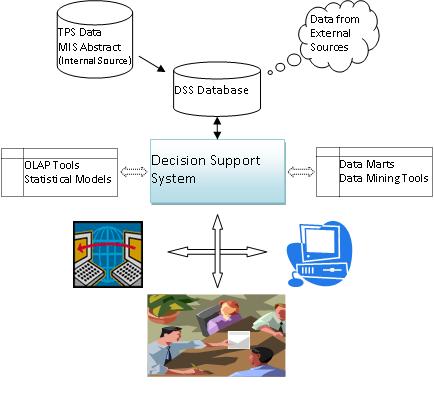
Fig. 3.3 Systematic overview of a DSS
3.8 SAP Enterprise Resource Planning
This term Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is used as a concept to integrate various activities of the organization to mange business efficiently. The basic purpose is to facilitate flow of information among various business functions within the organization. An integrated software application package known as ERP system is used to integrate all activities of an operation, product planning, development, manufacturing, finance, inventory, sales and marketing, customer relation, etc. ERP system provides all routine features of MIS and DSS to manage business efficiently as well as latest tools such as business data warehousing and business intelligence for mining novel information from historical data.
SAP is a software corporation which makes ERP systems. SAP stands for Systems Applications and Products. The original SAP idea was to provide customers with the ability to interact with a common corporate database for comprehensive range of applications which, includes managing their day to day operations, logistics, finances, month end, quarter end and yearly activities, reporting, HR, etc. SAP was initially designed to be run on the mainframe and was called R/2 (Release 2). Then quickly it shifted on to the client server model with a later release called R/3 and this was the most popular version of SAP. After R/3, later versions of their core software were launched called Enterprise Central Component (ECC). New modules to meet the growing need of organizations were added such as business intelligence (BI) to mine data from their daily operational data and extract meaningful trends that could enable further business opportunities, customer relationship management (CRM), Process integration (PI) etc.
With the development of WWW and Internet tools, SAP also moved from standard client server architecture to a completely web-based architecture where every transaction can be run from just a browser. Web based version is called as mySAP which is a very successful product in the market. A few best known software products of the company are:
· Enterprise resource planning application (SAP ERP),
· Enterprise data warehouse solution - SAP Business Warehouse, SAP Business Objects
· Sybase mobile products and in-memory computing appliance (SAP HANA).
· Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
· Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
· Supply Chain Management (SCM)
· Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
3.9 Applications in Dairy Industry and Animal Management
A large number of applications of DSS in animal management have been reported in literature at national and international level. A few important applications are mentioned here for reference as given below:
3.9.1 HERDMAN: A new preventive herd health software to enhance dairy animal productivity (Infovet; 302 Shariq Apt. Takoli, Kalwe, Thane, India 400 605, herdmancom@Hotmail.Com)
Vetindia Infotech Solutions, Mumbai, in collaboration with the Department of Medicine, Bombay Veterinary College, affiliated to Maharashtra Animal and Fishery Sciences University, has developed a cow / buffalo herd management software that is tailor-made to satisfy the needs of dairy industry as well as dairy farmers. It is a window-based software that provides computing and analysis strength using Visual Basic and Access/MS-SQL. Its interface is icon/menu driven which can be operated by a moderate literate farmer without any difficulty. Major characteristics of this software are:
· It maintains life-time records of animals in the farm
· Records of cows and buffaloes can be maintained simultaneously and data can be analyzed separately
· Records of all categories of animals, such as calves, heifers, adults, breeding bulls and working bullocks can be maintained
· The records of culled, sold or died animals maintained in archive files that can be retrieved easily to analyze data
It provides data integration and merging facility with other window-based software used for other purposes, such as, progeny testing, epidemiological mapping, GIS- or Info map-based data modules. HERDMAN can easily be interfaced with milking machines, milk parlor or automatic feeding machines.
3.9.2 Empowering dairy farmers through a dairy information & services kiosk
(http://unpan1.un.org/intradoc/groups/public/documents/UNPAN/UNPAN023605.pdf)
In recent years, milk co-operative movement initiated by National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) has led to a substantial increase in milk production in India. Two main reasons for this increase are efficient procedures for collection of milk and higher profits for producers. IT has played an important role in improving milk production of the country by educating the farmers and brining efficiency and transparency in the procedures. Automation of milk procurement and billing process at 2,500 rural milk collection societies has immensely benefitted the farmers. The DISK has enabled co-operatives and farmers to manage database of milch cattle and access to information about valued services about animal health, market trends, scientific animal management practices etc. These cases demonstrate that farmers are willing to invest in technology provided the farmers are empowered through innovative systems.