Module 6.
Elements of marketing mix – IV. promotion
Lesson 21
ADVERTISING
21.1 Introduction
There are various connotations of ‘advertising’ in marketing literature:
· The dissemination of information concerning an idea, service or product to compel action in accordance with the intent of the advertiser.
· Advertising is any paid form of non personal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods and services by an identified sponsor.
· Advertising is a message paid for by an identified sponsor and delivered through some medium of mass communication. Advertising is a persuasive communication.
· Advertising is controlled, identifiable information and persuasion by means of mass communication media.
· Advertising is the non personal communication of marketing related information to a target audience, usually paid for by the advertiser and delivered through mass medium in order to reach the specific objectives of the sponsor.
21.2 Objectives of Advertising
Advertising achieves two goals, one that of communicating and propagating the product and other of achieving the sales. Advertising objectives are classified as sales and communication objectives as given below:
21.2.1 Sales objectives
This are measured in terms of increase in sales, increase in market share and return on investment.
21.2.2 Communication objectives
It is related with increase in mind awareness, increase in comprehension, increase in brand attitude. Under Communication objectives, following specific communication objectives are performed by advertising.
21.2.2.1 Informing (Awareness generation)
The first and foremost task of all the advertisement is to inform the people and make them aware about the availability of the product or service and describe its characteristic features so as to explain what exactly is the product or services.
21.2.2.2 Persuasion for attitude formation (Forming Favorable
attitude)
The advertising message aim at forming favorable attitude about the brand and finally make the consumers to purchase the product. For e.g. Tide advertising in TV channels to show the product features.
21.2.2.3 Reinforcement of desired behavior (Customer loyalty)
In today’s competitive business world, each company tries to increase its market share. Thus, repeated marketing communication should strengthen customer loyalty and build referrals for future sales. For e.g. AMUL advertisements by Amul for their dairy products.
21.3 Categories of Advertising
Advertising can be categorized into following types:
21.3.1 National advertising vs. local advertising
The word ‘National advertising’ indicates that such advertising is not limited to any specific geographic location. Such advertisements are undertaken by branded products with the objective of informing or reminding consumers about the brand. This advertising attempts to create an image of the product among specific target audience. For example, advertisement by some of the car manufacturers target specific consumer segment. For e.g., Tata nano cars are advertising targeting the people with low budget. i.e. lower middle class people Local advertising has a limited regional focus. It is undertaken by retailers so as to develop store loyalty among consumers. Example: Advertisement by the retailer on the paper box. Duliram penda of Baroda give their advertisement on paper box.
21.3.2 Co-operative advertising
In such type of advertising, the manufacturer and dealer bear the cost of advertising. The dealers generally put the advertisements in local magazine. They are guided by manufacturers. For e.g. Honda twister advertisement in newspapers, magazine etc.
21.3.3 End product advertising
The advertisements of different raw materials/ component parts which become part of final product are called end product advertising. For e.g. MRF Tires advertising in channels and magazines.
21.3.4 Trade advertising
Such advertising is aimed at resellers to motivate them to stock the products. From mass distributed products, it is necessary that more and more retail stores sell the product so as to achieve maximum distribution. Thus, trade advertising is used to create brand awareness among retailers. For e.g. Basmati rice advertising on packaging bags
21.3.5 Industrial advertising
In case of industrial goods which are purchased by manufacturers to produce finished good, personal selling is generally used. Industrial advertisements help to reduce personal selling costs. Industrial advertisements are more specific, detailed and aimed at small number of experts. Industrial advertisements use industry publications, direct mail, telephone, trade fair and internet. For e.g. A4 size Oriental Xerox paper give their advertisement on it packaging material.
21.3.6 Professional advertising
Professional like medical consultants, engineers, architects etc make purchases for their clients (final consumers). Professional advertisements are aimed at such professional and use professional journals and direct mail. For e.g. Bansal classes of Kota for IIT JEE give advertisement in newspapers.
21.3.7 Non product advertising
Besides products, ideas and services are also advertised.
21.3.7.1 Idea
advertising
This advertising is used to sensitize general public towards some common subjects affecting the society e.g. polio eradication, save girl child, non discrimination of AIDS victims etc. For e.g. Gujarat tourism by Amitabh Bacchan on TV Channels
21.3.7.2 Service
advertising
With the progress of economy, there is also growth of service sector. Contribution of service sector in employment highlighting virtues of any particular service may be regarded as service advertising. For example, educational services, financial services etc. For e.g. Bajaj Allianz giving insurance advertisement on TV Channels
21.3.7.3 Corporate
or institutional advertising
This advertising is used to build the image of an institution or organization among its stakeholders e.g. sponsorship of any event by an institution. For e.g. Sharda university advertisement on TV Channels.
21.4 The Advertising Management Process
The advertising management process comprises of several distinct steps (Fig. 21.1):
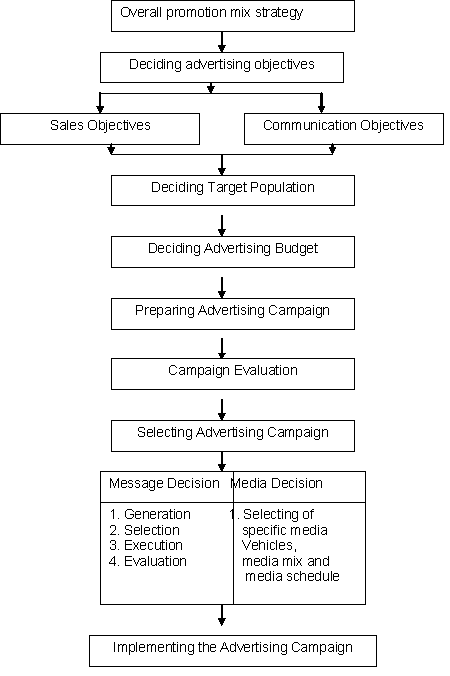
Fig. 21.1 Advertising management process
21.5 The Advertising Budget
There is no standard rule for deciding advertising budget. Following guidelines are taken into consideration while deciding advertising budget:
21.5.1 Competitor similarity
The common method employed by many companies is to set their advertising budget similar to major competitors. This method does not give any idea about company’s advertising needs and marketing needs.
21.5.2 Affordable
This method is adopted by many small organizations where in the allocate some advertising budget amount which they can afford. This amount is not fixed any may even get reduced to transfer of allocated advertising budget to more pressing needs.
21.5.3 Fixed percentage of turnover
Under this method, a fixed percentage of annual sales turnover is set as a part as advertising budget. The limitation of the method is that it does not take into consideration the product life cycle or the competitive situation.
21.5.4 Budget in relation to function
This method overcomes the limitations of previous methods, amount of funds required to achieve the specified advertising goals is decided on a function to function basis. The budget is allocated based upon market to market, product to product and brand to brand basis.
21.5.5 Statistical method
The firms may also employ some of the statistical method like regression analysis to decide advertising budget. This method uses part historical time series or cross sectional data to approve at budget estimates.
21.6 Comparison of Advertising Media
Table 21.1 highlights the advantages and disadvantages of major media types.
Table 21.1 Advantages and disadvantages of major media types
|
Media |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Television |
Mass Coverage |
Less selectivity |
|
High reach |
Short message span |
|
|
Mixed impact of sound, sight and action |
Higher total cost involved |
|
|
Less cost per exposure |
Lead to clutter |
|
|
Effective in drawing attention |
|
|
|
Radio |
Less cost |
Limited to local coverage |
|
High frequency |
Only audio |
|
|
More focus on selection segment |
Noise |
|
|
|
Less attention possibility |
|
|
|
Short life span and message. |
|
|
News Paper |
More coverage |
Short life |
|
More space with less cost |
Clutter |
|
|
Less lead time for ad placement |
Less attention Possibility |
|
|
More choice for ad position |
Selective exposure |
|
|
More suitable for current ads. |
No audio – video |
|
|
Exposure controlled by reader |
|
|
|
Possibility of inserting coupons |
|
|
|
Magazines |
Possibility to have more focus on selected segment |
More lead time for ad placing |
|
Longevity of information |
No audio – video |
|
|
More information quantum |
Less frequency |
|
|
Higher readership per copy |
Less flexibility |
|
|
Out door |
Suitable for specific location |
Short Message |
|
More repetition |
Short exposure time |
|
|
More visibility |
|
|
|
Direct Mail |
More selectivity possible |
More cost per contact clutter |
|
|
Exposure controlled by reader |
Possibility of throwing as junk mail |
|
|
More information Content |
|
|
|
Possibility of repetition |
|
|
Internet |
Controlled by use |
Less reach in developing countries |
|
|
More attention and involvement |
|