Module 8. International marketing
Lesson 31
DECIDING THE MARKETING ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE
31.1 Introduction
An International Company carries out its activities in several countries. It is necessary to decide about the optimum organization structure. Organizational planning will cover aspects of type of organizational structure to be adopted, scope and extent of responsibility. Organizational structure reflects company's policies viz degree of control, hierarchy, chain and command and communication etc. Thus there is no standard organizational structure; many international companies face problems of inappropriate hapazard lines of authority, improper communication channels within various levels of organization as well as between main central office in domestic country and branches in other countries.
31.2 Types of Organization Structure
International companies are required to increase the profits by increasing the sale in foreign markets while maximizing sales in domestic market also. There are following options available to international companies to organize their operations.
(i) Product divisions
(ii) Geographic divisions
(iii) Matrix Organization
Product division type of organization structure is responsible for product sale in all the markets. This type of structure is suitable for those companies which have diverse product line and are also witnessing faster growth.
Geographic division structure is solely responsible for all products and functions within a specified geographic area. Such a structure is suitable when a close relationship between national and local government is desired.
Matrix organization structure consist either a product division or geographic division with centralized functional staff or a combination of area operations and global product management. A matrix organization structure is preferred by international companies as it provides number of advantages. It facilitates sharing of experiences, technology, information, expertise and resources among different business units and the company.
Apart from these major three distinct organizational structures, international companies may also adopt a special structure wherein company is basically organized by product lines but there are further geographic sub classifications or product categories. The structure is supported by functional staff at various levels.
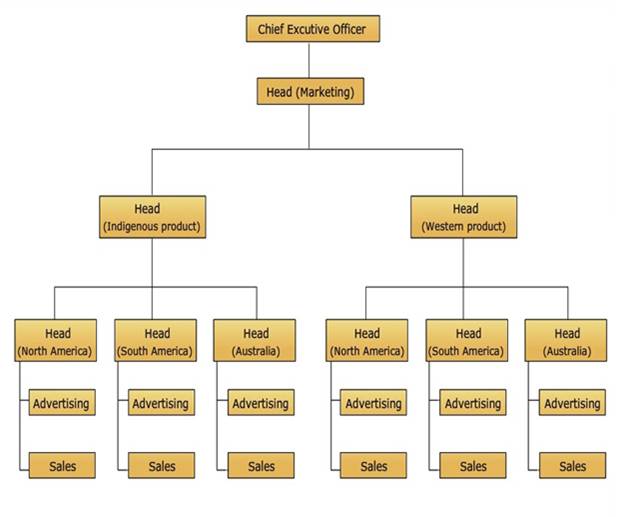
Fig. 31.1 Combination of product, geographic and functional approach
31.3 Type of Organizational Structures
31.3.1 International division structure
When any Company enters the international market, initially it has less number of products and also it has less knowledge and limited experience of international market. Thus most of the companies start with international division. Except Product activities all other activities viz marketing, finance etc are carried out by international division. Products are manufactured by the normal domestic organizational structure and then simply turned over as such to the international division.
31.3.1.1 Advantages
1. Efficient means for inexperienced companies.
2. Allows for specialization and training in international marketing.
3. Able to adopt more focused strategy due to access to topmost official based on reporting relationship.
31.3.1.2 Disadvantages
1. Not self sufficient as dependent on other department for necessary support.
2. Low importance due to fewer sales.
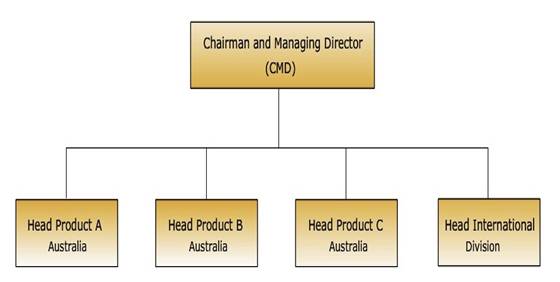
Fig. 31.2 International division structure
31.3.2 Global functional structure
In this, the structure is formed around all major functions of organization viz. marketing, finance, production etc. As structure is for international business, this functional department has global responsibility. This structure is most appropriate when organization is selling same product at all the countries.
31.3.2.1 Advantages
1. Decreases conflicts between headquarter and overseas center as functional departments are responsible for global operations.
2. Better control and coordination from head quarter.
3. Increases global orientation of all functional managers.
31.3.2.2 Disadvantages
1. Not suitable for organization selling wide variety and products in international market.
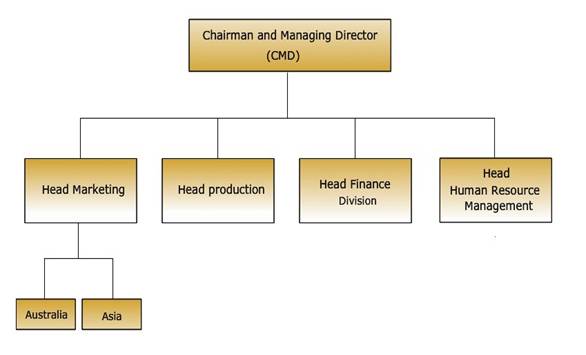
Fig. 31.3 Global functional structures
31.3.3 Global area structure
In this case structure is organized around different geographic locations of the world. The managers of this geographical location are responsible for functional activities of their respective geographical area.
31.3.3.1 Advantages
1. Provides opportunity for deep learning by concerned managers.
2. Leads to improved performance as each area is considered as a profit center and concerned manager is specifically responsible for performance.
31.3.3.2 Disadvantages
1. Prevent Coordination and Communication between different geographic areas.
2. Firm is not able to achieve economies of scale due to duplication of all activities including production.

Fig. 31.4 Global area structure
31.3.4 Global product structure
Here the structure is organized around different products. Each separate product division is supported by all functional departments and is generally regarded as a profit center.
31.3.4.1 Advantages
1. Leads to functional coordination due to their responsibility for a single product.
2. Provides opportunities for improvement of product due to focused approach on single product.
31.3.4.2 Disadvantages
1. Wastage of resources due to duplication of all functional support to each individual product.
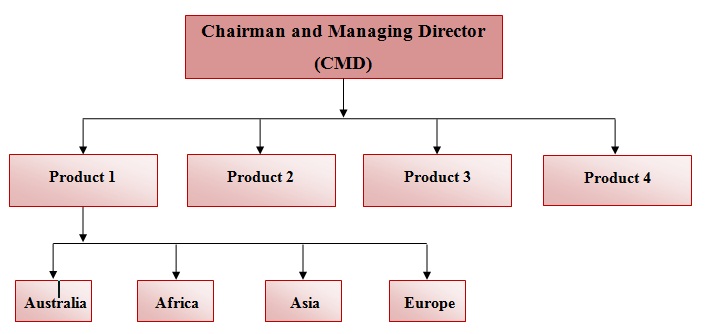
Fig. 31.5 Global product structure
31.3.5 Global division structure
In this structure all functional activities are placed within each division and each division has got global responsibility. Here a division consists of group of related products.
31.3.5.1 Advantages
1. Reduces wastage of resources by avoiding duplication of resources by assigning them in common to all products of a division.
31.3.5.2 Disadvantages
1. Difficult to determine global and local element of a product. These obscure opportunities for leveraging global advantages in raw material procurement, advertising etc.

Fig. 31.6 Global division structure
31.3.6 Global customer structure
This is organized around different customer groups having different needs.
31.3.6.1 Advantage
1. Provides opportunity for deep understanding of different customer segments.
31.3.6.2 Disadvantage
1. Wastage of resources due to duplication of resources across division can occur.
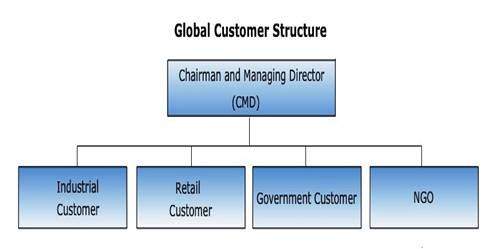
Fig. 31.7 Global customer structures
31.3.7 Global matrix structure
In this type two organization structure are superimposed on each which creates dual reporting relationships.
31.3.7.1 Advantages
1. Facilitates Communication by flow of information throughout the organization.
2. Balanced orientation due to superimposition of two separate departments.
31.3.7.2 Disadvantages
1. Due to dual reporting relationship chances and conflict increases.
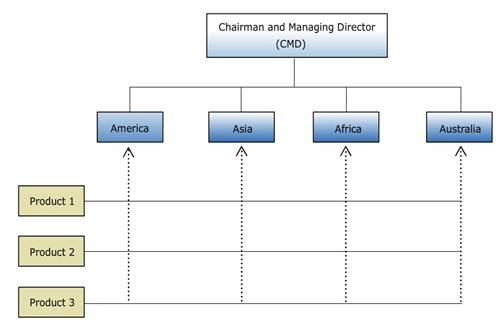
Fig. 31.8 Global matrix structure
31.4 Conclusion
An international
company adopts a suitable organizational structure based upon its policy and resources.
The adopted structure falls in the category of centralized or decentralized
structure. Both the approaches has its relative advantages and disadvantages.
Centralization offers the advantage of marketing specialist available at one
place, provides necessary control at planning and implementation phase easy to
create a centralized database. In decentralized approach, responsible managers
are given complete antinomy and they implement suitable region specific
marketing policies.
Global environment is very dynamic and therefore international companies always try to use a right type of organizational structure which provides necessary flexibility to respond immediately to local needs and also provide appropriate control over regional branches away from the main headquarter.