| Home |
ONION |
MAJOR PESTS |
| 1. Onion thrips |
| 2. Onion maggot |
| 3. Earwig |
POTENTIAL MAJOR PESTS |
| 1. Tobacco caterpillar |
| 2. Cutworm |
| Questions |
| Download Notes |
PEST OF ONION :: MAJOR PESTS :: ONION MAGGOT
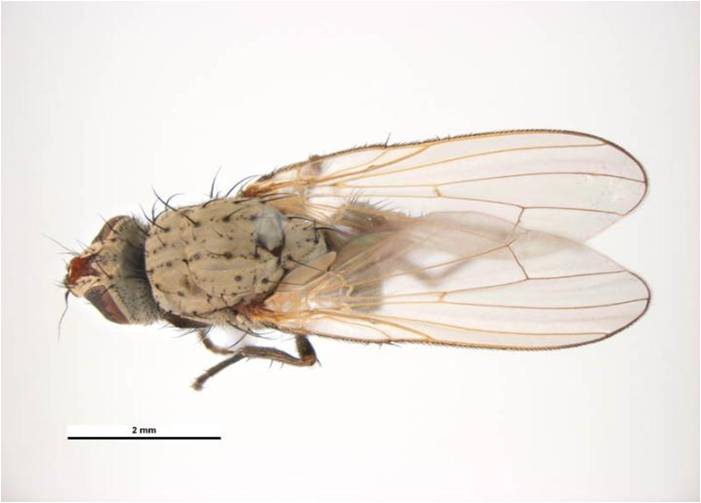
2. Onion Maggot: Delia antiqua (Anthomyiidae: Diptera)
Distribution and status: Widely distributed in France, Germany, Canada, USA, Japan, erstwhile USSR and England. This pest also attacks onions in northern India.
Host range: Onion and garlic
Damage symptoms
The maggots bore into the bulbs, causing the plants to become flabby and yellowish. It causes withering in the field and rotting in storage. Damage leads to the invasion of Bacillus carolovorus which causes soft rot of onion
 |
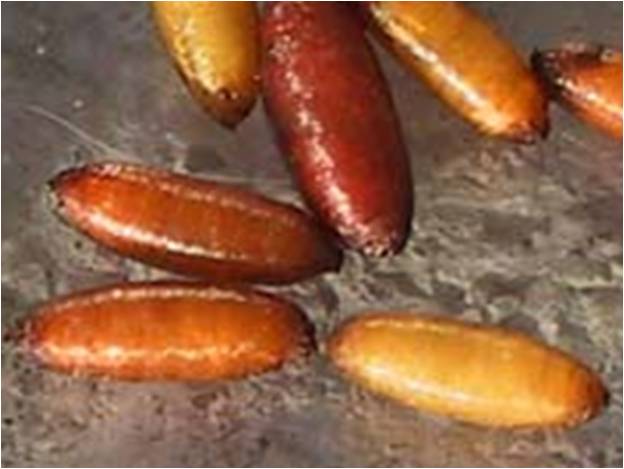
Bionomics : The flies are slender, greyish, large-winged. The maggots are small, white and about 8 mm. in length. The female lays elongate, white eggs near the base of the plant, in cracks in the soil. The eggs hatch in 2-7 days. The maggots crawl up, enter the leaf sheath and reach the bulb. They feed there and become full-grown in 2-3 weeks. The maggots then crawl out of the bulb and pupate in the soil. After 2-3 weeks, the adults emerge and start the new generation. In the third generation, the pest often attacks the onions shortly before the harvest. It initiates the process of rotting of the onions in storage.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Delia antiqua |
Delia antiqua |
Delia antiqua |
Delia antiqua |
Management
Grow Allium fistulosum as it is more tolerant than A. cepa .Apply 10 kg of carbaryl 4G or phorate lOG to the soil followed by light irrigation.
Spray methy demeton 25 EC or dimethaote 30 EC 1.0 L in 500 – 750 L of water per ha.