Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1
Module 2.
Module 3.
Module 4
LESSON 1. Familiarization with different makes and models of 4-wheeled tractors Study of points to be checked daily, starting and safety checks
Introduction:
The tractor is a prime-mover which can be used for carrying out farm operations such as ploughing; harrowing, seeding, inter-cultivation, harvesting, transportation, land levelling and operating stationary machines (, irrigation pumps, threshers, chaff cutters, cane crusher etc.) All the machines require periodical servicing, maintenance and repairs for efficient and economical performance to stay in good operating conditions throughout working life. Although, most of the tractor manufacturers have appointed their dealers to provide operational know how, after sales and services of their products, yet, these are inadequate. Consequently, many machines are not properly maintained and are subjected to abnormal break downs, wear and tear and thereby reducing the effective life of the machines.
Due to improper maintenance and servicing of the tractors, it has been found that many tractors have been rendered unserviceable within a short period of 5000 hours or even less. Seizures of engine, due to lack of oil in the sump and overheating of engine due to inadequate water in the radiator are common troubles. Damage of front wheel bearings and other moving parts due to improper lubrication and adjustments have also been seen often. A typical 4-wheel general purpose tractor is shown in Fig: 1. below:

Let us familiarize ourselves with different controls of common four wheel tractor before deliberating more on its maintenance.
1. Tractor Assembly & Controls:
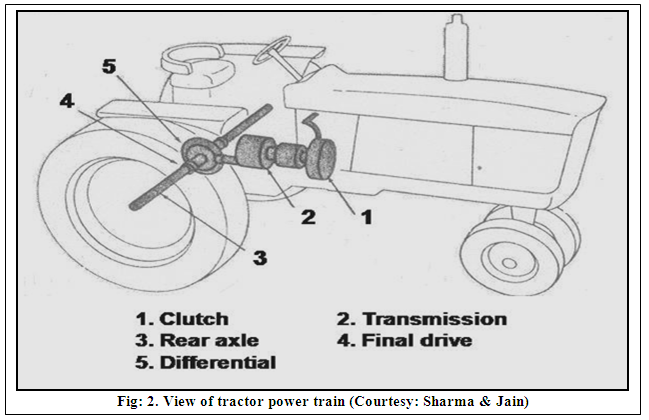
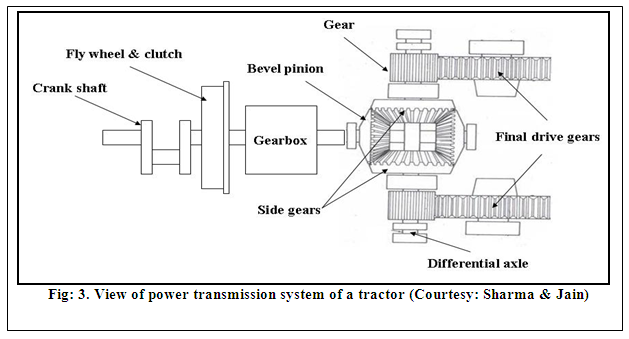
1.1 Power Trains: The power trains consist of engine, clutch, transmission (gear box), differential, final drives, axle shafts, wheels or tracks, steering & brakes.
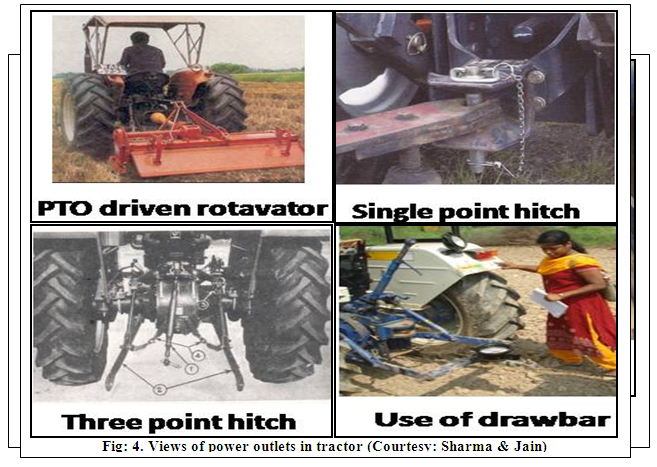
1.2 Power outlets: The tractor power is made available for use through hydraulic lift, drawbar hitch, belt pulley & PTO shaft. (Fig: 4.)
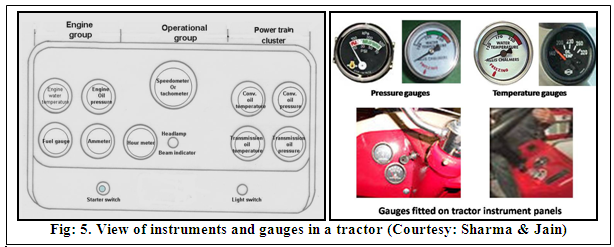
1.3 Instruments and gauges: Most of the tractors are equipped with gauges and meters such as fuel pressure gauge, oil pressure gauge, water temperature gauge, hour meter, hydraulic pressure gauge and temperature gauge to indicate their operating conditions. Starter switch, light switch, horn button, fuel cut off controls is also fixed on many tractors (Fig: 5.).
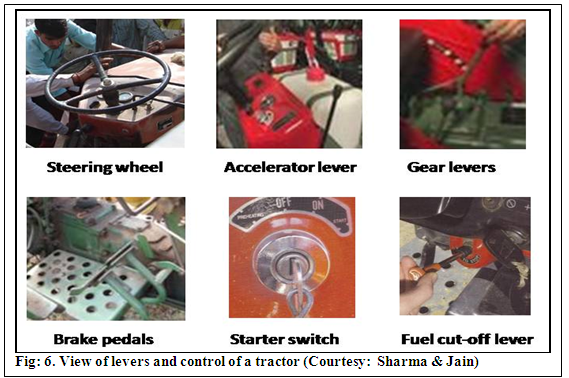
1.4 Levers and controls: The tractor is also provided with throttle or accelerator lever/ pedal, clutch pedal/ lever, brake pedal/ lever, gear shift lever (main & auxiliary), steering wheel/ lever, hydraulic control, PTO pulley lever, differential lock/ pedal/ lever etc. to exercise control on different operations (Fig: 6.).
Daily, starting and safety checks in tractor:
Daily check points for starting and safety in tractor are:
- Check fuel in fuel tank (is there enough fuel to complete the task).
- Check coolant level in the radiator, or inspect cooling fins on air cooled models of tractor.
- Check tire inflation pressure (refers to owner’s manual for proper inflation of front and rear tyres for each job).
- Check the condition of the tyres. Look for cuts, cracks and buckling.
- Check the battery, cables and terminals and electrolyte level.
- Check the transmission and hydraulic oil levels.
- Check air filter elements, or the oil level in an oil bath type air cleaner.
- Check the guards and shields to ensure that they are correctly installed and in good conditions.
- Check operator’s station. Be sure that it is clear of spilled fuel, oil, grease, crop residue, or loose objects.
- Check the lighting system and ensure “Slow Moving Vehicle Emblem “is placed.
Steps for starting a Tractor:
- Make necessary checks before mounting on the tractor.
- Mount the tractor from the left side of the tractor
- Sit down on the seat
- Make necessary checks after sitting on the seat
- Move the hand accelerator to half of its total travel
- Put the key into the main switch and turn it clockwise to warm the engine with heater (if required).
- Turn the key further clockwise to crank the engine.
- If the engine does not start within 10-20 seconds, repeat cranking of the engine after about 30 seconds.
- Keep the engine running till it is warmed-up (for 2-3 minutes).
- Disengage the clutch by pressing the clutch pedal.
- Select suitable gear depending on speed and load requirement.
- Release parking brake.
- Increase engine speed by moving throttle lever clockwise and slowly release the clutch pedal, until the tractor moves off.
- Take off the foot from the clutch pedal.
- To change gear (up or down) reduce the engine speed by moving the hand throttle anti-clockwise.
- Press the clutch pedal and let the tractor come to stop position (or crawling speed) Select the desired gear and repeat step 13.
Steps for stopping a Tractor:
- Reduce the engine speed (by hand throttle lever) to idling position.
- Press the clutch pedal to disengage the clutch and put the gear shift lever in neutral position.
- Release the clutch.
- Stop the tractor (by applying brakes)
- Pull the fuel shut-off knob/ stop switch till engine stops.
- Withdraw key by turning it anticlockwise.
- Engage parking brake.
- Get up from the seat
- Get down from the tractor from left side only.
Tractor operation safety precautions
a) General Points:
- Run and maintain the tractor according to the operator’s Manual of Tractor provided by the tractor manufacturer.
- Check the working of all controls just after riding the tractor.
- Release the parking brakes before starting.
- Be alert and alert to drive it safely.
- Whenever the tractor is stopped, even for a short while gear-shift lever should be brought to neutral position.
- Always park the tractor with gear shift lever in the neutral position and with parking brake applied.
- Operate the tractor smoothly; avoid jerky starts, turns and stops.
- Drive slowly in difficult conditions.
- Look at the rear while reversing the tractor.
- Attend immediately to oil and fuel leakages.
- Listen to the noise or sound in the engine, power transmission, etc., if any abnormal noise is noticed stop the tractor and investigate the causes.
- Always keep a watch ahead of the tractor.
- When stopped put the tractor out of gear, set brakes firmly.
- Refuel the tractor only when the engine is cool, don't spill fuel and never smoke while refuelling.
- Hitch implements only to drawbar or specified hitch points of the tractor.
- Air intake assembly must be removed before raising the bonnet.
- Beware of oily steps & slippery platforms.
- Never drive after taking alcohol drink or drugs.
- Never run the tractor engine in a closed shed or garage.
- Don't permit unauthorised' persons to ride the tractor unnecessarily.
- Never operate the hand accelerator of tractor from the ground.
- Do not allow the tractor wheels to run over sharp objects.
- Do not keep foot (ride) on the clutch and brake pedals while the tractor is running.
- Do not sit or stand on the implement when the tractor is in motion.
- Do not attempt the dual selector lever when the tractor is in motion.
- Avoid spilling fuel over the engine.
- Avoid overloading of the tractor during operations.
- Do not get off or on the tractor when it is in motion.
- Do not remove the radiator cap while the engine is hot.
- Never leave the key in the starting switch.
b) Points to be considered for safety on the Farm
- Set the wheels as wide as required for the job. Use wider wheel track on slopes for stability.
- Add weights on rear or front, as the case may be, for proper traction.
- Keep P.T.O. and belt pulley shields in proper place.
- Do not hook load at a point above the drawbar.
- Reverse the tractor in low gear.
- Driver tractor in low gears while overcoming obstacles like small bunds and ditches.
- Draft control should not be used for raising or lowering the implements at the end of trip/ row.
- Do not ride the drawbar of tractor during operation.
c) Points for Road Safety
- Obey the traffic rules while driving on road.
- Drive slowly while making turns.
- Use lower gear during up and down-hill driving.
- Be careful during road crossing.
- Stop the tractor on the left side of the road.
- Keep brake pedals interlocked when driving on the road.
- Give way to automobile vehicles.
- While driving at night with trolley, do make extensive provision for lights at the rear as well as on the sides.
- Never coast down- hill in neutral gear.
- Never depress clutch pedal while driving down-hill.
- Do not tend to turn sharply using independent brakes when travelling at high speeds.
- Do not overload trolley.
- Do not drive without rear-view mirrors
References:
Sharma D N. & S. Mukesh (2004). Design of Agricultural Tractor (Principles and Problems) Book Pub. Jain Brothers, New Delhi
Wadhwa D.S., Dhingra H. S. & Santokh, Singh Field operation and maintenance of tractor and farm machinery (FMP-301), laboratory manual by, Department of Farm Machinery and Power Engineering, PAU Ludhiana
Service and Maintenance Manual of Tractor by Escorts Ltd., Faridabad