Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1. Role of mechanization and its relationsh...
Module 2. Performance and power analysis
Module 3. Cost analysis of machinery- fixed cost a...
Module 4. Selection of optimum machinery and repla...
Module 5. Break-even point and its analysis, relia...
Module 6. Mechanization planning
Module 7. Case studies and agricultural mechanizat...
Topic 8
Topic 9
Topic 10
Lesson 22. Utilities and reliability index
Utility index: It is a direct indication of work machine contact hours. With an increase in the utility index the cost of operation and the non-operating hours decrease. This in turn, results into a net increase in the total power available for farm work. Utility index (K) can be calculated as
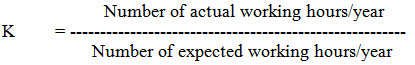
Reliability index: This index measures the percentage of assurance of proper working of tractors. It is determined as follows:
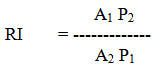
Where,
RI = Reliability index
A1 = Breakdown charges available = 0.04 nP
A2 = Breakdown charges - actual incurred
P1 = Penalty for breakdown = 0.25 x 10-3 B P
P2 = Money blocked in storing the requisite spare parts
P = New cost of tractor
n = Number of years of breakdown occurrence since purchase
B = Number of breakdown hours
Thus,
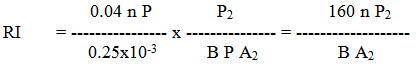
The optimum reliability index is determined by assuming P2/A2 = 1. Although P2/A2 is not exactly equal to 1 and it keeps on fluctuating but in an Indian condition through previous experience it has been observed that on an average P2 is more or less equal to A2. Thus, above equation can be rewritten as
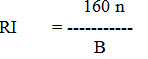
If we take reliability index 1, then B = 160 n
If n = 15 years for tractor
B = 160 x 15 = 2400 hours
This indicates that in order to maintain an optimum reliability index, the total number of breakdown hours in the life time of tractor must not exceed 2400 hours