Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1. Classification of Farm Power Sources
Module 2. Classification of IC Engines & Therm...
Module 3. Performance Characteristics
Module 4. Engine Components
Module 5. Engine Operating System
Module 6.:Engine Fuel System
Module 7. Engine Governor
Module 8. Engine Cooling & Lubrication system
Module 9. Engine Ignition System
LESSON 6. ENGINE TERMINOLOGY & DEFINITIONS
6.1 Bore: The inner diameter of the cylinder is known as the bore which is actually equal to sum of the diameter of the piston and a very small clearance between the piston and cylinder wall.
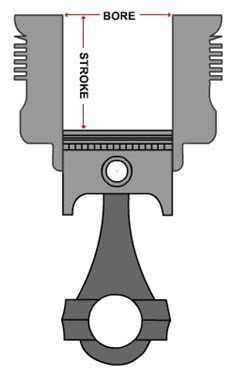
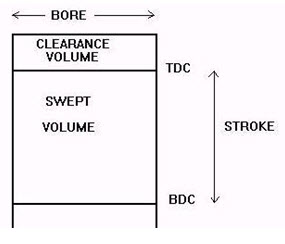
6.2 Stroke: Movement distance of the piston from one extreme position to the other: TDC to BDC or BDC to TDC.
6.3 Clearance volume: Minimum Volume in the combustion chamber with piston at TDC is called clearance volume.
6.4 Displacement volume: Volume displaced by the piston as it travels through one stroke i.e TDC to BDC or BDC to TDC. Displacement can be given for one cylinder or for the entire engine (displacement in one cylinder multiplied by number of cylinders). Displacement volume is also known as swept volume.
6.5 Compression ratio : It is the ratio of total cylinder volume with piston at BDC (Piston displacement + clearance volume) to the combustion chamber volume (clearance volume) with piston at TDC. Compression ratio varies from 14:1 to 20:1 for diesel engine and 4:1 to 8:1 for petrol engines.
6.6 Ignition Delay (ID): Time interval between ignition initiation and the actual start of combustion is called ignition delay..
6.7 Air Fuel Ratio: Ratio of mass air to mass of fuel input into engine. The power generation by the engine varies with the air fuel ratio. Due to slow burning of too lean mixture of fuel causes loss of power. Maximum economy lies between 13.5:1 to 15:1 air fuel ratio.