Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1. Moisture content and its determination.
Module 2. EMC
Module 3. Drying Theory and Mechanism of drying
Module 4. Air pressure within the grain bed, Shred...
Module 6. Study of different types of dryers- perf...
Module 5. Different methods of drying including pu...
Module 7. Study of drying and dehydration of agric...
Module 8. Types and causes of spoilage in storage.
Module 9. Storage of perishable products, function...
Module 10. Calculation of refrigeration load.
Module 11. Conditions for modified atmospheric sto...
Module 12. Storage of grains: destructive agents, ...
Module 13. Storage of cereal grains and their prod...
Module 14. Storage condition for various fruits an...
Module 15. Economics aspect of storage
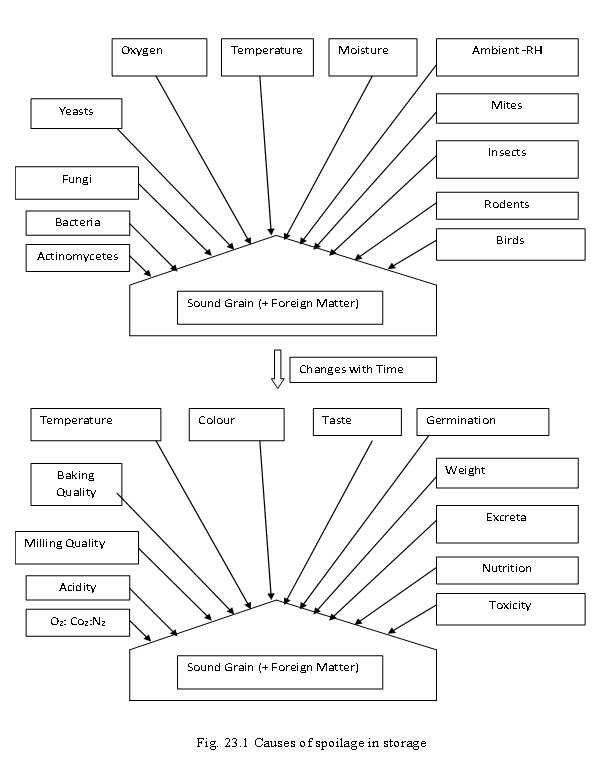
Lesson 23. Causes of spoilage in storage
Following are the various sources causing spoilage in the stored food and corrective measures are required to be exercised to minimize the effect to alleviate the effects.
23.1 Mechanical Damage
Causes
incorrect harvesting methods
Poor handling, threshing, shelling, cleaning, sorting or drying
Bad transport and loading practices (e.g. use of hooks)
Effects
Losses in weight
Losses in quality (germination power, nutritional value)
increased vulnerability to infestation from insect pests, fungi and rodents
Countermeasures
Pay attention to maximum temperatures when drying
Use safe techniques in harvesting, transport, processing and storage
Take care when handling bags
Repair or replace damaged bags
Do not use hooks to carry bags
Repair pallets (e.g. protruding nails!)
23.2 Heat
Causes
Unsuitable storage structures (false location, insufficient shade and ventilation facilities, lack of heat insulation)
Mass reproduction of storage pests and fungi
Lack of aeration of store
High moisture content of the grain
Effects
Losses in weight
Losses in quality (nutritional value, germination power)
Good conditions for pest development
Condensation with subsequent development of fungi
Countermeasures
Build suitable storage structures
Provide shade for stores or silos (e.g. by means of wide eaves or shading trees)
Keep temperatures as low as possible (aerate storage facility)
Conduct treatments for pest control
Store bags on pallets in order to improve aeration
Maintain spaces of 1 m around all bag stacks
23.3 Moisture
Causes
insufficient drying before storage
High relative humidity
Constructional faults and damage to the store (unsuitable materials, unsealed floor, walls and roof, holes, gaps, etc.)
imbalances in temperature (e.g. day/night) in storage facility with subsequent condensation
Produce stored on the floor or touching the walls
Mass reproduction of pests
Effects
Losses in quality
Losses in weight
Development of fungi and formation of mycotoxins
improved conditions for the development of pests
Swelling and germination of seeds
Damage to storage structures
Countermeasures
Dry produce sufficiently before storage
Repair and seal storage facility
Keep relative humidity as low as possible in storage facility (perform controlled ventilation)
Store bags on pallets
Maintain spaces of 1 m around all bag stacks
Conduct pest control treatments
Avoid temperature fluctuations (day/night) in store by means of shade and ventilation
23.4 Insect Pests
Causes of infestation
- introduction of infested lots
- Cross infestation from neighboring lots or stores
- Migration from waste or rubbish
- Hiding places in stores (cracks, fissures)
- Use of infested bags
Effects
Losses in weight
Losses in quality (impurities such as droppings, cocoons and parts of insects, reduction of nutritional value, reduction in germination power)
increase of temperature and moisture
Countermeasures
Harvest at the right time
Choose tolerant varieties
Keep means of transportation clean
Remove infested cobs, panicles or pods before storage
Ensure that produce is dry before storing
Prevent pest introduction by checking for infestation before storing
Clean the store daily
Keep the temperature and relative humidity as low as possible (perform controlled ventilation)
Prevent any pest infiltration by sealing the store (windows, doors, ventilation facilities; e.g. with the use of insect gauze)
Repair any damage to the store immediately
Store old and new lots separately
Clean empty bags thoroughly and treat them against insects if necessary
Perform pest control treatments
Rotate stocks: 'first in first out'
23.5 Microorganisms
Causes of infestation
High moisture content of stored produce
High relative humidity in store
Condensation
Humidity and moisture produced by insects
Effects
Loss of quality (smell, taste, colour, nutritional value, germination power)
Formation of mycotoxins
Slight loss of weight (mould)
Further increase in temperature and moisture
Further condensation
Countermeasures
Dry produce sufficiently before storage
Keep relative humidity as low as possible in storage facility (perform controlled ventilation)
Store bags on pallets
Maintain spaces of 1 m around all stacks
Conduct pest control treatments
23.6 Rodents
Causes of infestation
Penetration through badly closing doors, windows, ventilation openings, holes
Lack of barriers
Lack of hygiene in store and surrounding area (possible hiding and breeding places)
Effects
Loss of weight
High losses in quality due to contamination of produce with faeces and urine
Contamination of produce with pathogenic agents (typhoid, rabies, hepatitis, plague, etc.)
Damage of material and facilities (bags, doors, electric cables)
Countermeasures
Prevent entry of rodents by sealing store rat-proof
Keep store and surrounding area clean
Place traps
Carry out rodent control measures
23.7 Birds
Causes of infestation
- Open or broken doors, windows, ventilation openings or roofs
Effects
Losses in weight
Damage to bags
Contamination of stored produce with droppings and pathogenic agents
Countermeasures
Bird-proof stores (carry out repair work, fit grilles or nets)
Remove any nests of granivore birds from the store and surrounding area
23.8 References
-
A Text Book of Unit Operations Agricultural Processing by K.M Sahay and K.K.Singh.
-
FAO Corporate document Repository Produced by Agriculture and consumer Protection.
-
Sinha, R.N &Muir. Grain Storage: Part of a System. Avi Publisher.