Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
MODULE 1. FLUIDS MECHANICS
MODULE 2. PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
MODULE 3. PRESSURE AND ITS MEASUREMENT
MODULE 4. PASCAL’S LAW
MODULE 5. PRESSURE FORCES ON PLANE AND CURVED SUR...
MODULE 6.
MODULE 7. BUOYANCY, METACENTRE AND METACENTRIC HEI...
MODULE 8. KINEMATICS OF FLUID FLOW
MODULE 9: CIRCULATION AND VORTICITY
MODULE 10.
MODULE 11.
MODULE 12, 13. FLUID DYNAMICS
MODULE 14.
MODULE 15. LAMINAR AND TURBULENT FLOW IN PIPES
MODULE 16. GENERAL EQUATION FOR HEAD LOSS-DARCY EQ...
MODULE 17.
MODULE 18. MAJOR AND MINOR HYDRAULIC LOSSES THROUG...
MODULE 19.
MODULE 20.
MODULE 21. DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND SIMILITUDE
MODULE 22. INTRODUCTION TO FLUID MACHINERY
LESSON 20. VENTURIMETER, ORIFICEMETER AND NOZZLE, SIPHON FLOWRATE MEASUREMENT
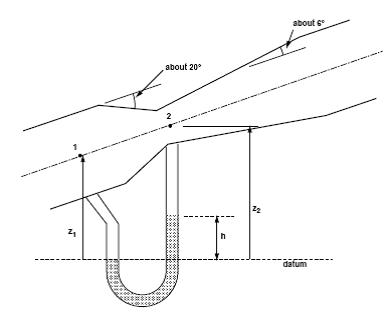
venturimeter
-
The Venturi meter is a device for measuring discharge in a pipe.
-
It is a rapidly converging section which increases the velocity of flow and hence reduces the pressure.
-
It then returns to the original dimensions of the pipe by a gently diverging ‘diffuser’ section.
Apply Bernoulli along the streamline from point 1 to point 2
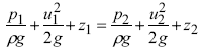
By continuity
![]()
![]()
Substituting and rearranging gives
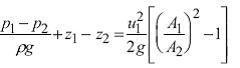
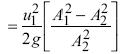
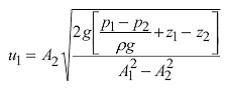
The theoretical (ideal) discharge is u×A.
Actual discharge takes into account the losses due to friction, we include a coefficient of discharge (Cd ≈ 0.9)
![]()
![]()
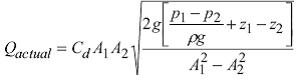
In terms of the manometer readings
![]()
![]()
Giving
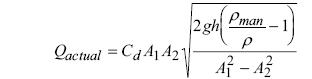
This expression does not include any elevation terms. (z1 or z2) When used with a manometer
The Venturimeter can be used without knowing its angle.
Last modified: Monday, 16 September 2013, 6:55 AM