Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1. Management Concepts & Principle
Module 2. Management Functions
Module 3. Marketing Management
Module 4. Concepts and application of management p...
Module 5. Production, Consumption, Processing and ...
Module 6. Meaning & Theories of International ...
Module 7. WTO provisions for trade in agricultural...
12 April - 18 April
19 April - 25 April
26 April - 2 May
Lesson-31 Cooperative Agricultural Marketing
31.1 INTRODUCTION
For a country like India having a very large population, the co-operative way of working in business and commercial activities is the only way of social upliftment. Prof. D. R. Gadgil said, “Though Co-operation has failed, Co-operation MUST Succeed”. The importance of this can be understood as “Agricultural cooperatives: key to feeding the world” was the 2012 World Food Day theme, in recognition of the role cooperatives play in improving food security and contributing to the eradication of hunger. In this lesson, we will discuss the meaning and objective of marketing cooperatives and the role of National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation (NAFED)
31.2 COOPERATIVE MARKETING-MEANING
Cooperative marketing organizations are association of producers for the collective marketing of their produce and for securing for the members the advantages that result from large-scale business which an individual cultivator cannot secure because if his small marketable surplus.
In a co operative marketing society, the control of the organization is in the hands of the farmers, and each member has one vote irrespective of the number of shares purchased by him. The profit earned by the society is distributed among the members on the basis of the quantity of the produce marketed by him. In other words, co operative marketing societies are established for the purpose collectively marketing the products of the member farmers. It emphasizes the concept of commercialization. Its economic motives and character distinguish it from other associations. These societies resemble private business organization in the method of their operations: but they differ from the capitalistic system chiefly in their motives and organizations. An example of successful cooperative in India is dairy sector which has drawn worldwide accolades for its achievement.
31.3 FUNCTIONS
The main functions of co operative marketing societies are:
To market the produce of the members of the society at fair prices;
To safeguard the members for excessive marketing costs and malpractices;
To make credit facilities available to the members against the security of the produce brought for sale;
To make arrangements for the scientific storage of the members‟ produce;
To provide facilities of the grading and market information which may help them to get a good price for their produce
To introduce the system of pooling so as to acquire a better bargaining power than the individual members having a small quantity of produce for marketing purposes;
To act as an agent of the government for the procurement of food grains and for the implementation of the price support policy
To arrange for the export of the produce of the members so that they may get better returns;
To make arrangements for the transport of the produce of the members from the villages to the market on collective basis and bring about a reduction in the transportation; and
To arrange for the supply of the inputs required by the farmers, such as improved seeds, fertilizers, insecticides and pesticides.
The advantages that co-operative marketing can confer on the farmer are multifarious, some of which are listed below.
Increases bargaining strength of the farmers: Many of the defects of the present agricultural marketing system arise because often one ignorant and illiterate farmer (as an individual) has to face well-organised mass of clever intermediaries. If the farmers join hands and for a co-operative, naturally they will be less prone to exploitation and malpractices. Instead of marketing their produce separately, they will market it together through one agency.
Direct dealing with final buyers: The co-operatives can altogether skip the intermediaries and enter into direct relations with the final buyers. This practice will eliminate exploiters and ensure fair prices to both the producers and the consumers.
Provision of credit: The marketing co-operative societies provide credit to the farmers to save them from the necessity of selling their produce immediately after harvesting. This ensures better returns to the farmers.
Easier and cheaper transport: Bulk transport of agricultural produce by the societies is often easier and cheaper. Sometimes the societies have their own means of transport.
Storage facilities: The co-operative marketing societies generally have storage facilities. Thus the farmers can wait for better prices.
Grading and standardization: This task can be done more easily for a co-operative agency than for an individual farmer. For this purpose, they can seek assistance from the government or can even evolve their own grading arrangements.
Market intelligence: The co-operatives can arrange to obtain data on market prices, demand and supply and other related information from the markets on a regular basis and can plan their activities accordingly.
Influencing marketing prices: Wherever strong marketing co-operative are operative, they have bargained for and have achieved, better prices for their agricultural produce.
Provision of inputs and consumer goods: The co-operative marketing societies can easily arrange for bulk purchase of agricultural inputs, like seeds, manures fertilizers etc. and consumer goods at relatively lower price and can then distribute them to the members.
Processing of agricultural produce: The co-operative societies can undertake processing activities like crushing seeds, ginning 'and pressing of cotton, etc. In addition to all these advantages, the co-operative marketing system can arouse the spirit of self-confidence and collective action in the farmers without which the programme of agricultural development, howsoever well conceived and implemented, holds no promise to success.
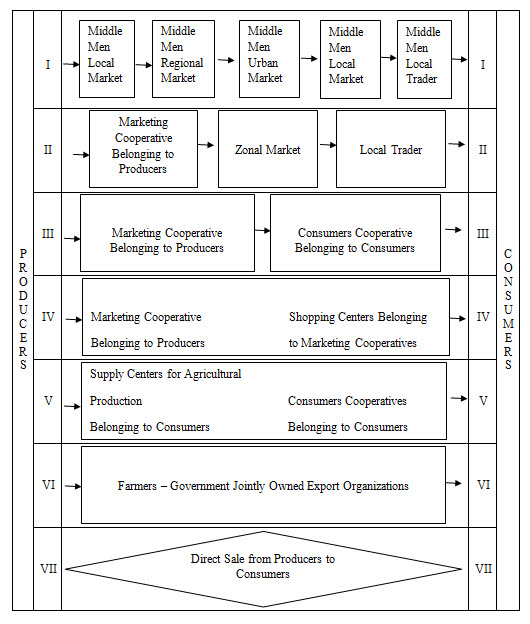
31.4 COOPERATIVE MARKETING MODELS:
Following is the schematic representation of different models of Marketing Cooperative
31.5 NATIONAL AGRICULTURAL COOPERATIVE MARKETING FEDERATION (NAFED)
Nafed is registered under the Multi State Co-operative Societies Act. Nafed was setup with the object to promote Co-operative marketing of Agricultural Produce to benefit the farmers. Agricultural farmers are the main members of Nafed, who have the authority to say in the form of members of the General Body in the working of Nafed.
Objectives
The objectives of the NAFED shall be
To organise, promote and develop marketing, processing and storage of agricultural, horticultural and forest produce,
To distribute agricultural machinery, implements and other inputs,
Undertake inter-State, import and export trade, wholesale or retail as the case may be.
To act and assist for technical advice in agricultural production for the promotion and the working of its members and cooperative marketing, processing and supply societies in India.
In furtherance of these objectives, the NAFED may undertake one or more of the following functions/ activities:
To facilitate, coordinate and promote the marketing and trading activities of the cooperative institutions in agricultural and other commodities, articles and goods;
To undertake or promote on its own or on behalf of its member Institutions or the Government or Government Organisations, Inter-State and international trade and commerce and undertake, wherever necessary, sale, purchase, import, export and distribution of agricultural commodities, horticultural and forest produce.
To undertake purchase, sale and supply of agricultural products, marketing and processing requisites, such as manure, seeds, fertiliser, agricultural implements and machinery, packing machinery, construction requisites, processing machinery for agricultural commodities, forest produce, dairy, wool and other animal products;
To act as warehouseman under the Warehousing Act and own and construct its own godowns and cold storages;
To act as agent of any Government agency or cooperative institution, for the purchase, sale, storage and distribution of agricultural, horticultural, forest and animal husbandry produce, wool, agricultural requisites and other consumer goods;
To act as insurance agent and to undertake all such work which is incidental to the same;
To organise consultancy work in various fields for the benefit of the cooperative institutions in general and for its members in particular;
To undertake manufacture of agricultural machinery and implements, processing, packing, etc. and other production requisites and consumer articles.
To set up storage units for storing various commodities and goods, by itself or in collaboration with any other agency in India or abroad;
To maintain transport units of its own or in collaboration with any other organisation in India or abroad for movement of goods on land, sea, air etc.;
To collaborate with any international agency or a foreign body for development of cooperative marketing, processing and other activities for mutual advantage in India or abroad;
To undertake marketing research and dissemination of market intelligence;
To subscribe to the share capital of other cooperative institutions as well as other public, joint and private sector enterprises if and when considered necessary for fulfilling the objectives of NAFED.
To arrange for the training of employees of marketing/processing/supply cooperative societies;
To maintain common cadres/pools of managerial/technical personnel required by the marketing/processing/supply cooperative societies;
To establish processing units for processing of agricultural, horticultural and forest produce and wool;
To undertake grading, packing and standardisation of agricultural produce and other articles;
To acquire, take on lease or hire, lands, buildings, fixtures and vehicles and to sell, give on lease or hire them for the business of NAFED.
To advance loans to its members and other cooperative institutions on the security of goods or otherwise;
To guarantee loans or advances or give undertakings to any Society or Company in which the Federation has a shareholding or financial involvement as a promoter to be able to assist its development or expansion or for starting any industrial undertaking by such societies/companies;
To guarantee loans or advances or give undertakings on behalf of any such society or company as mentioned above to any financing institutions:
To do all such things or undertake such other business or activities as may be incidental or conducive to the attainment of any or all of the above objects.