Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
MODULE 1. Fundamentals of Soil Mechanics
MODULE 2. Stress and Strength
MODULE 3. Compaction, Seepage and Consolidation of...
MODULE 4. Earth pressure, Slope Stability and Soil...
Keywords
29 March - 4 April
5 April - 11 April
12 April - 18 April
19 April - 25 April
26 April - 2 May
LESSON 32. Bore Hole Spacing and Depth
32.1 How many Bore Holes?
The number of bore holes depends on:
(i) Type and size of the project
(ii) Budget for site investigation
(iii) Soil variability
The bore holes have to be located where the loads are expected.
32.2 SPACING OF BORINGS (Das, 1999)
Type of project Spacing (m)
Multistory buildings 10 – 30
One-story industrial plants 20 – 60
Highways 250-500
Residential subdivision 250-500
Dams and dikes 40 - 80
32.3 Minimum depth of boring (ASCE, 1972)
-
Determine the net increase of stress, Δσ, under the foundation (as shown in Figure 1)
-
Estimate the variation of the vertical effective stress, σ'v , with depth
-
Determine the depth D = D1, at which stress increase Δσ = q/10, where q = estimated net stress on the foundation
-
Determine the depth D = D2, at which Δσ/ σ'v = 0.05.
-
Unless bedrock is encountered, the smaller of the two depths, D1 and D2 will be the approximate minimum depth of boring required.
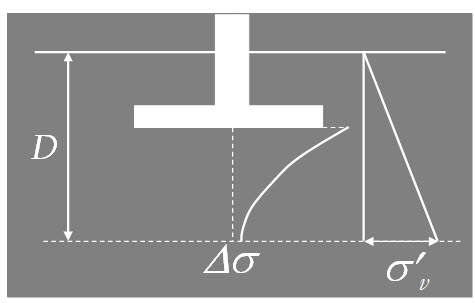
Fig. 32.1.
The minimum depth of boring for a building with a width of 30.5 m (100 ft) will be as follows (Sowers and Sowers, 1970)
No of stories Boring depth
1 3.5 m
2 6.0 m
3 10 m
4 16 m
5 24 m
32.3.1. Depth of Borings (according to IS 1892-1979)
Type of foundation Depth of boring
1. Isolated spread footing or raft One and half times the width (B) of the foundation
2. Adjacent footings with clear spacing One and half times the length (L) of
less than twice the width footing
3. Pile and well foundation To a depth of one and half times the width of structure from the bearing level (toe of pile or bottom of well)
4. (a) road cut Equal to the bottom width of the cut
(b) Fill Two meters below ground level or equal to the height of the fill whichever is greater.
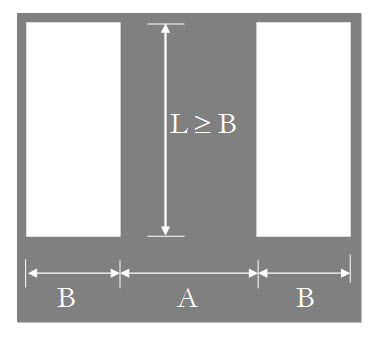
D = 1.5 B for A ³ 4B and D = 1.5 L for A < 2B
D = 3 B for A >2B and <4B
D = 4.5 B for A < 2B
D = 1.5 B for A ³ 4B
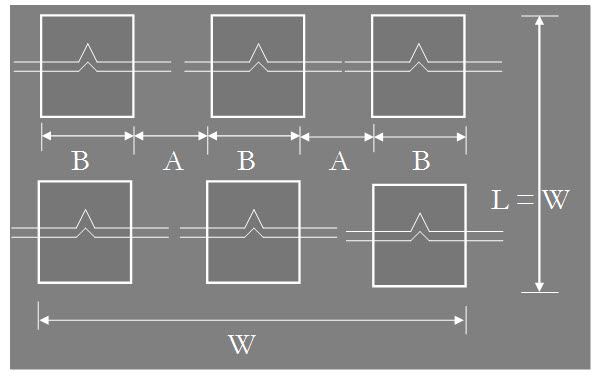 Fig. 32.2 Depth of boring according to IS 1892-1979.
Fig. 32.2 Depth of boring according to IS 1892-1979.
References
Ranjan, G. and Rao, A.S.R. (2000). Basic and Applied Soil Mechanics. New Age International Publisher, New Delhi, India
PPT of Professor N. Sivakugan, JCU, Australia
Suggested Readings
Ranjan, G. and Rao, A.S.R. (2000) Basic and Applied Soil Mechanics. New Age International Publisher, New Delhi, India.
Arora, K.R. (2003) Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Standard Publishers Distributors, New Delhi, India.
Murthy V.N.S (1996) A Text Book of Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, UBS Publishers’ Distributors Ltd. New Delhi, India.
PPT of Professor N. Sivakugan, JCU, Australia (pnu-foundation-engineering.wikispaces.com/.../Site+Investigatioon+PPT.pdf).
Das, B.M. (1999). Principles of Foundation Engineering. PWS Publishing, USA.
IS1892-1979. Indian Standard. CODE OF PRACTICE FOR SUBSURFACE INVESTIGATION FOR FOUNDATIONS.