Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 3. Marketing Management
Lesson 11. Marketing Environment
11.1 INTRODUCTION
Marketers need to be good at building relationships with customers, others in the company and external partners. To do this effectively, they must understand the major environmental forces that surround all of these relationships. A company’s marketing environment consists of the actors and forces outside marketing that affect marketing management’s ability to build and maintain successful relationships with target customers. The marketing environment is made up of a microenvironment and a macroenvironment. The microenvironment consists of the actors close to the company that affect its ability to serve its customers-the company, suppliers, marketing intermediaries, customer markets, competitors and publics. The macro- environment consists of the larger societal forces that affect the microenvironment-demographic, economic, natural, technological, political and cultural forces. Let us look first at company’s micro-environment.
11.2 COMPANY’S MICROEVIRONMENT
Marketing management’s job is to build relationships with customers by creating customer value and satisfaction. However, marketing managers cannot do this alone. Marketing success will require building relationships with other company departments, suppliers, marketing intermediaries, customers, competitors and various publics which combine to make up the company’s value delivery network. Figure 11.1 shows these major actors in the marketer’s microenvironment.
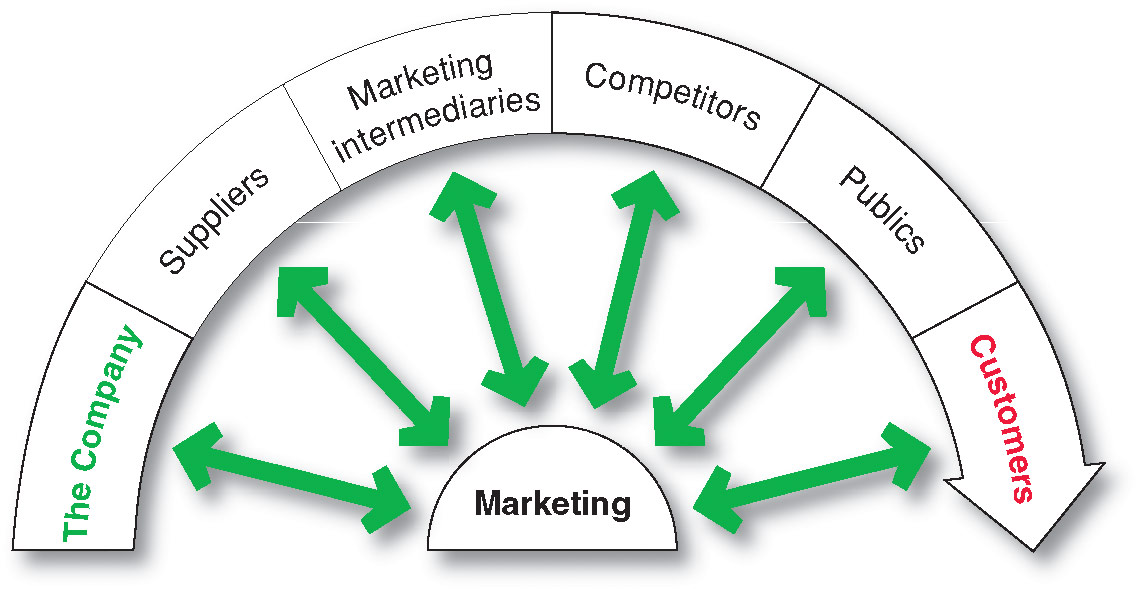
Figure 11.1: Actors in microenvironment
-
The company: In designing marketing plans, marketing management takes other company groups into account-groups such as top management, finance, research and development (R&D), purchasing, operations and accounting. Top management sets the company’s mission, objectives, broad strategies, and policies. Marketing managers make decisions within the strategies and plans made by top management. Marketing management must work closely with other company departments.
-
Suppliers: Suppliers form an important link in the company’s overall customer value delivery system. They provide the resources needed by the company to produce its goods and services. Supplier problems can seriously affect marketing. Marketing managers must watch supply availability-supply shortages or delays, labor strikes and other events can cost sales in the short run and damage customer satisfaction in the long run. Most marketers today treat their suppliers as partners in creating and delivering customer value.
-
Marketing Intermediaries: Marketing Intermediaries help company to promote, sell and distribute its products to final buyers. They include resellers, physical distribution firms, marketing services agencies and financial intermediaries. Resellers are distribution channel firms that help the company find customers or make sales to them. These include wholesalers and retailers, who buy and resell merchandise. Physical distribution firms help the company to stock and move goods from their points or origin to their destinations. Working with warehouse and transportations firms, a company must determine the best ways to store and ship goods balancing factors such as cost, delivery, speed and safety. Marketing services agencies are the marketing research firms, advertising agencies, media firms and marketing consulting firms that help the company target and promote its products to the right markets. Financial intermediaries include banks, credit companies, insurance companies and other businesses that help finance transactions or insure against the risks associated with the buying and selling of goods.
-
Customers: The Company needs to study following types of customer markets closely. Consumer markets, Business markets, Government markets, Global markets. Each market type has special characteristics that call for careful study by the seller.
-
Competitors: The marketing concept states that to be successful, a company must provide greater customer value and satisfaction that its competitors do. Thus marketers must do more that simply adapt to the needs of target consumers. They also must gain strategic advantage by positioning their offerings strongly against competitors’ offerings in the minds of consumers.
-
Public: Public is a group that has an actual or potential interests in or impact on an organisation’s ability to achieve its objectives. The types of public are financial publics, media publics, government publics, citizen-action publics, local publics, general public and internal public.
11.3 THE COMPANY’S MACROENVIRONMENT
The company and all of the other actors operate in a larger macro-environment of forces that shape opportunities and pose threats to the company. Figure 11.2 shows the important actors in macroenvironment. In this section these external forces are discussed.
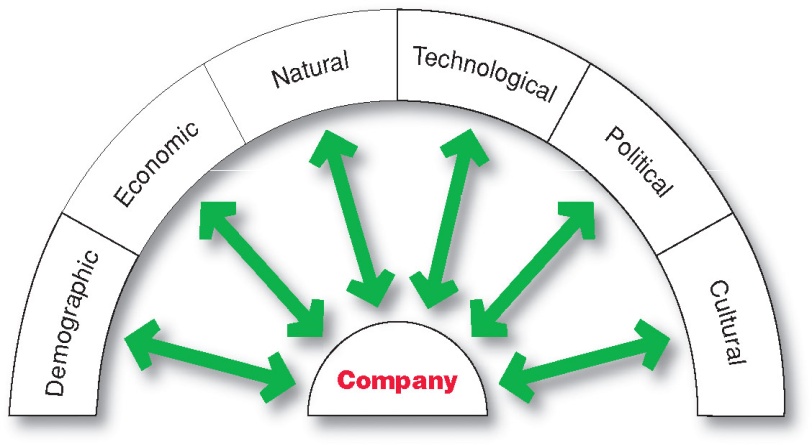 Figure 11.2: Actors in macroenvironment
Figure 11.2: Actors in macroenvironment
-
Demographic Environment: Demography is the study of human populations in terms of size, density, location, age, gender, race, occupation and other statistics. The demographic environment is of major interest to marketers because it involves people and people make up markets.
-
Changing age structure of the population: The needs of the customer depend on the age group. The needs of the children will be different from the adult and the old. Therefore, it is very important for the company to study the age group of the customer it wants to target. For example, presently India has the one of the highest young population in the world. A successful company should produce goods to satisfy the need of this group.
-
Changing family system: One need to understand the family structure prevailing the country. In India, the traditional joint family system is gradually replaced by the nuclear families. The needs of the nuclear families are different from the joint families.
-
Migratory population: Migration of people from one state to another state and one country to another country in search of better standard of life is a common phenomenon. One can see people across the India in cities like Mumbai, Bangalore, and Hyderabad etc. A company manager needs to recognize this fact and plan his marketing strategy accordingly.
-
Economic Environment: This consists of factors that affect consumer buying power and spending pattern. Following are the some of the major economic trends in India.
-
Changes in income: The disposal personal income of people has increased many folds in recent years. Therefore, people are spending heavily on consumer goods.
-
Changing consumer spending patterns:As the income increases the percentage spent on food declines, the percentage spent on housing remains about constant and both percentage spent on most other categories and that devoted to savings increases. Even among the income spent on food, more expenditure is on value added products like, fruits, vegetables, eggs, meat etc.
-
-
Natural Environment: Natural resources that are needed as inputs by marketers or that are affected by marketing activities.
-
Technological Environment: Forces that create new technologies, creating new product and market opportunities. Technological environment changes rapidly. Change from film to digital camera has resulted in loosing market leader status for some companies. One who do not foresee coming of the new technology will have to face the adverse consequences.
-
Political Environment: Marketing decisions are strongly affected by developments in the political environment. The political environment consists of laws, government agencies and pressure groups that influence or limit various organizations and individuals in a given society.
-
Cultural Environment: It is made of institutional and other forces that affect a society that shapes their basic beliefs, values, perceptions, preferences and behaviors. People grow up in a particular society that shapes their basic beliefs and values. They absorb a worldview that defines their relationships with others.
-
Language: The importance of language differences cannot be overemphasized, as there are almost 3,000 languages in the world. Language differences cause many problems for marketers in designing advertising campaigns and product labels. Language problems become even more serious once the people of a country speak several languages. For example, in Canada, labels must be in both English and French. In India, there are over 200 different dialects, and a similar situation exists in China. Figure 1
-
Colors: Colors have different meanings in different cultures. For example, in Egypt, the country's national color of green is considered unacceptable for packaging, because religious leaders once wore it. In Japan, black and white are colors of mourning and should not be used on a product's package. Similarly, purple is unacceptable in Hispanic nations because it is associated with death.
-
Customs and Taboos: All cultures have their own unique set of customs and taboos. It is important for marketers to learn about these customs and taboos so that they will know what is acceptable and what is not for their marketing programs.
-
Values: An individual's personal values arise from his/her moral or religious beliefs and are learned through experiences. For example, in America we place a very high value on material well-being, and are more likely to purchase status symbols than people in India. Similarly, in India, the Hindu religion forbids the consumption of beef, and fast-food restaurants such as McDonald's and Burger King would encounter tremendous difficulties without product modification. Additionally, Americans spend large amounts of money on soap, deodorant, and mouthwash because of the value placed on personal cleanliness.
-
Aesthetics: The phrase "Beauty is in the eye of the beholder" is a very appropriate description for the differences in aesthetics that exist between cultures. For example, Americans believe that suntans are attractive, youthful, and healthy; however, the Japanese do not.
-
Time: Americans seem to be fanatical about time when compared to other cultures. Punctuality and deadlines are routine business practices in the U.S. However, salespeople who set definite appointments for sales calls in the Middle East and Latin America will have a lot of time on their hands, as business people from both of these cultures are far less bound by time constraints. To many of these cultures, setting a deadline such as "I have to know next week" is considered pushy and rude.
-
Business Norms: Business norms also vary from one country to the next and may present challenges to foreigners not used to operating within the particular norms of the host country
-
Religious Beliefs: Religion can affect shopping patterns and products purchased, in addition to the consumers' values, as discussed earlier. In the United States and other Christian nations, Christmas time is a major sales period. But for other religions, religious holidays do not serve as popular times for purchasing products. Women do not participate in household buying decisions in countries whose religion serves as opposition to women's rights.
-
Every culture has a social structure, but some seem less widely defined than others. That is, it is more difficult to move upward in a social structure that is rigid. For example, in the U.S., the two-wage-earner family has led to the development of a more affluent set of consumers. But in other cultures, it is considered unacceptable for women to work outside the home.
-