Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
MODULE 1. Orhtographic Projections of Machine comp...
MODULE 2. Types of joints
MODULE 3. Computer Aided drawing
MODULE 4. Numeric control systems
Topic 5
Topic 6
Topic 7
Topic 8
Topic 9
Topic 10
LESSON 1. 1st And 3rd Angle Methods Of Projection
1.1. INTRODUCTION
The method of describing an object is by words. But for the purpose of manufacture, it has to be described in terms of drawing. It gives the description of an object with respect to the shape and size. It gives the clear details of the
1.2. What is projection?
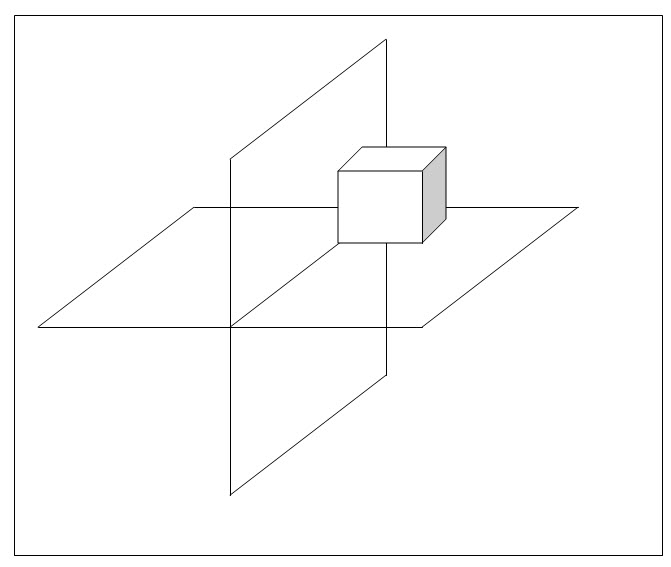
The outline of any object drawn on a paper in two dimensions is said to be a projection of the particular object on that plane. The object may be a point, a straight line or a solid. Suppose we have an object in between our eye and the drawing sheet, we just form the outline of the object that is visible to the eye on the drawing sheet, then the drawing or view on the paper is said to be the projection of the object on the plane. This process is accomplished by projecting straight lines from the eye to the paper or plane touching the contours of the object. The straight lines are known as projectors. The plane on which the object is projected and the view is drawn is known as plane of projection. These planes are considered to be transparent so that the object can be kept either in front of the plane or behind the plane and the projections are drawn on the plane.
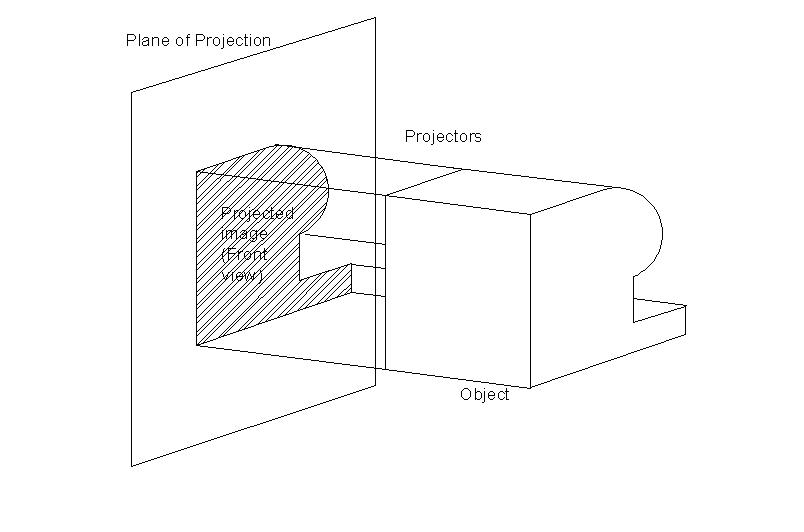 Fig.1.2.1. Projection of an Object in a Plane
Fig.1.2.1. Projection of an Object in a Plane
1.3.Different types of projections
I.Pictorial projections
When the projected image of the object gives the complete explanation of the object in one view, then the view is known as pictorial projection. This gives an idea about the shape and details of the object, but not the true dimensions of the object.
1.Perspective projection
It is the appearance of objects, buildings, etc, relative to each other, as determined by their distance from the viewer, or the effects of this distance on their appearance.
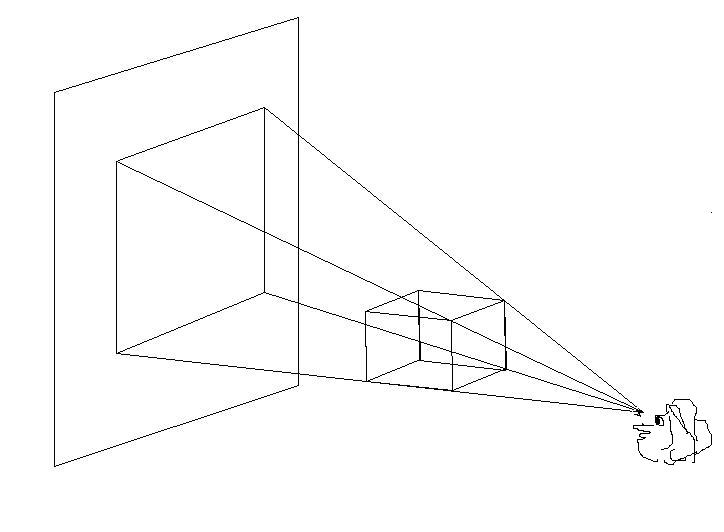
Fig.1.3.1. Perspective Projection of an Object in a Plane
2.Isometric projection
In this type of projection, the three edges of a solid right angle of an object are shown by means of three lines parallel to the isometric axes which meet at a point and make an angle of 120º with each other. It has been derived from the Greek. isos "equal" + metron "measure". Originally this was a method of using perspective in drawing.
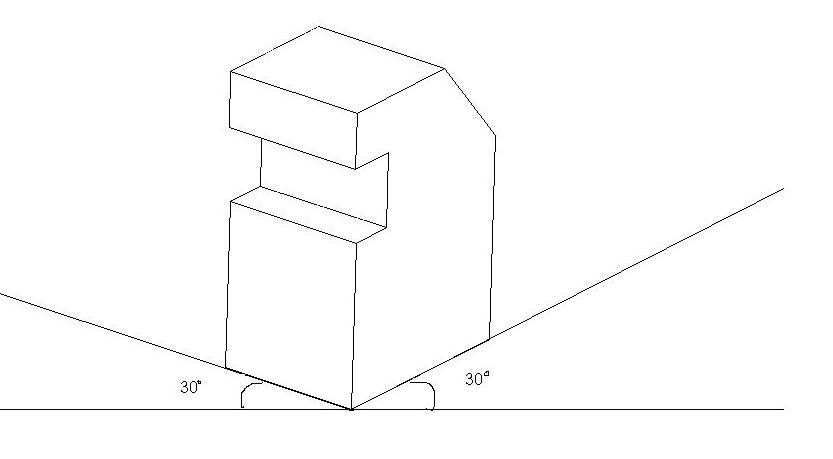
Fig.1.3.2. Isometric Projection of an Object
3.Oblique projection
When the object is assumed to be placed with one face parallel to the plane of projection, then the projection is known as Oblique projection. Here, the face parallel to the plane of projection appears in true shape and size.
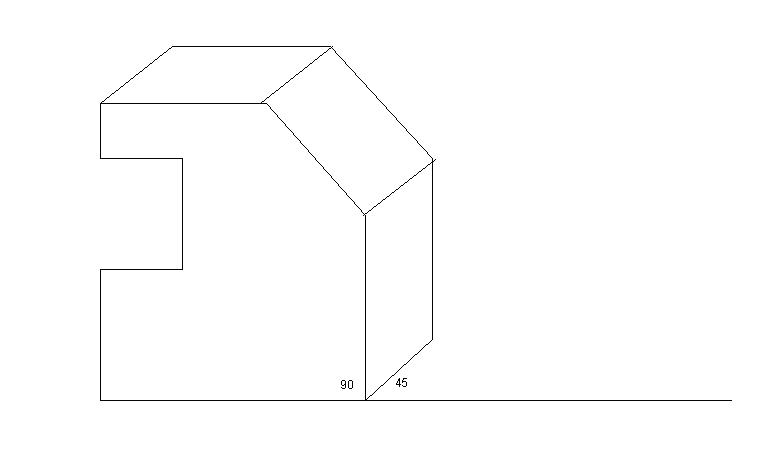
Fig.1.3.3. Oblique Projection of an Object
4.Orthographic projection
Ortho is a Greek word meaning “straight,” “upright,” “right,” “correct”
Orthographic is right angled drawing. When the projectors are perpendicular to the plane on which the projected image is obtained, it is known as Orthographic projecton.
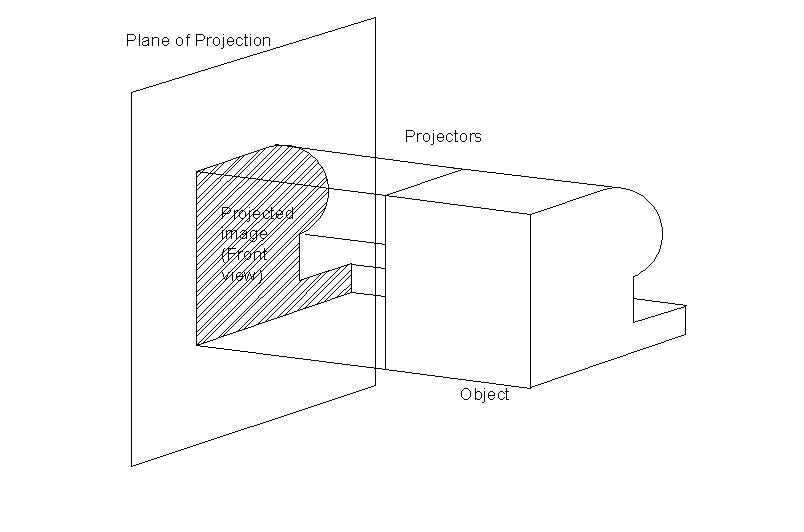
Fig.1.3.4. Orthographic Projection of an Object
(View animation)
1.4.First angle Projection
When the Object is in the First Quadrant, i.e., above the vertical plane and in front of the Horizontal plane, and then projected on the vertical plane and horizontal planes, then this projection is called first angle projection method. In the drawing, the first angle projection is represented by the symbol
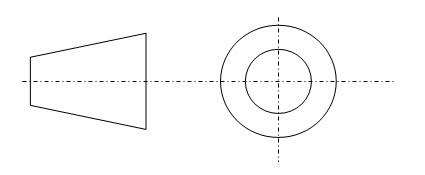
1.5.Third angle projection
When the object is kept in the third quadrant, i.e., below the horizontal plane and behind the vertical plane, and the projections are in the horizontal plane and vertical plane, then it is known as third angle projection. the drawing is represented by the symbol,