Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1. Role of mechanization and its relationsh...
Module 2. Performance and power analysis
Module 3. Cost analysis of machinery- fixed cost a...
Module 4. Selection of optimum machinery and repla...
Module 5. Break-even point and its analysis, relia...
Module 6. Mechanization planning
Module 7. Case studies and agricultural mechanizat...
Topic 8
Topic 9
Topic 10
Lesson 12. Interest on Investment
A large expensive item after depreciation for agricultural machinery is the interest. It is a direct expense item on borrowed capital. Even if cash is paid for purchased machinery, money is tied up that might be available for use elsewhere in the business. Interest rates vary considerably but usually are between 12 and 16 percent. Annual interest is calculated on an average investment by using the prevailing interest rate by the following formula:
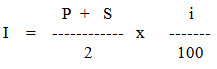
Where,
I = annual interest charge, Rs./year
P = purchase price, Rs.
S = salvage value, Rs.
i = interest rate, per cent
Insurance and Shelter
Insurance and shelter charges together are taken @ 2% of the purchase price per year.
Consideration of Inflation in Depreciation Analysis of Farm Equipment
Any consideration of cash flows in today’s economy must include an effect of inflation. Inflation can be defined in terms of an annual percentage that represents the rate at which current years prices have increased over the previous year’s prices. It has a compounding effect. Because of inflation, the cost of farm equipment or any other product continues to rise. Hence, inflation affects adversely the purchasing power of money. The future prices of farm equipment in the nth year at constant inflation rate can be represented by
F = P (1 + I)n ---------------- (1)
Where.
F = Future price in the nth year, Rs.
P = Purchase price, Rs.
I = Inflation rate, fraction
If the inflation changes in each year, then the future price of the farm equipment would be
F = P (1 + I1) (1 + I2) ---------- (1 + In) --------------- (2)
If constant inflation rate is taken as 10%, then the future price of the product after 10 years would be (using equation 1)
F = P (1 + 0.1)10 = 2.59 P
i.e. the future price of the product will inflate to 2.59 times the purchase price in 10 years.
The effect of inflation can be included in the depreciation analysis. The depreciation of a machine under constant inflationary condition using straight-line method can be written as

Where,
CDn = Cumulative depreciation charges up to nth year, Rs.
n = Number of years elapsed after the purchase of the machine
L = Life of machine, years
P = Purchase price, Rs.
S = Salvage value of the machine
Annual depreciation charge (Dn) in the nth year will be
Dn = CDn - CDn-1
and future value of machine at the end of nth year (Vn)
Vn = Future price at the end of nth year - CDn
= P (1 + I)n n - n/L [ P (1 + I)n - S ]
Taking life of the machine as 15 years and salvage value as 10% of the inflated price of the machine, equation (3) reduces to
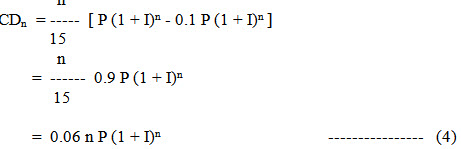
Similarly, cumulative depreciation charge up to (n-1)th year may be written as
CDn-1 = 0.06 (n-1) P ( 1 + I)n-1 --------------- (5 )
Annual depreciation charge (Dn) in the nth year will be
Dn = CDn - CDn-1
= 0.06 n P (1 + I)n - 0.06 (n-1) P ( 1 + I)n-1
= 0.06 P [ n (1 + I)n - (n-1) ( 1 + I)n-1 ] ------------- (6)
The remaining value of the machine after nth year (Vn ) may be obtained as
Vn = Future price at the end of nth year - cumulative depreciation value up to nth year
= P (1 + I)n - Dn
= P (1 + I)n - 0.06 n P (1 + I)n
= P (1 + I)n [ 1 - 0.06 n ] -------------- (7)
Variation in future price, total depreciation cost and remaining value of a machine as a function of purchase price P at constant 10% annual inflation rate under straight-line method for total life of machine 15 years are given in Table 2.
Table 2: Comparison of future price, depreciation cost and remaining value of machine as a function of purchase price.
|
End of year |
Future price |
Total depreciation |
Remaining value |
|
1 |
1.100 P |
0.0660 P |
1.0340 P |
|
2 |
1.210 P |
0.1452 P |
1.0648 P |
|
3 |
1.331 P |
0.2396 P |
1.0914 P |
|
4 |
1.464 P |
0.3514 P |
1.1126 P |
|
5 |
1.611 P |
0.4833 P |
1.1277 P |
|
6 |
1.772 P |
0.6379 P |
1.1341 P |
|
7 |
1.949 P |
0.8186 P |
1.1304 P |
|
8 |
2.144 P |
1.0291 P |
1.1149 P |
|
9 |
2.358 P |
1.2733 P |
1.0847 P |
|
10 |
2.594 P |
1.5564 P |
1.0376 P |
|
11 |
2.853 P |
1.8830 P |
0.9700 P |
|
12 |
3.138 P |
2.2594 P |
0.8786 P |
|
13 |
3.452 P |
2.6926 P |
0.7594 P |
|
14 |
3.797 P |
3.1895 P |
0.6075 P |
|
15 |
4.177 P |
3.7593 P |
0.4177 P |