Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1
Module 2.
Module 3.
Module 4
22 March - 28 March
29 March - 4 April
5 April - 11 April
12 April - 18 April
19 April - 25 April
26 April - 2 May
LESSON 2. Familiarization with service schedule, periodical service, 10 hours service schedule.
It is uneconomical to manufacture a tractor with materials which will run for the designed service life. Scientists in developed countries have developed car engines which can be used for 0.2-0.4 million km without changing lubrication oil. Pre-greased, sealed bearings having lubrication enough for the designed lives are available. Car tyres have service life of 80,000 to 1, 00,000 km. So, day is not far when vehicles may not require any maintenance. However, at present the materials used in manufacturing of tractors wear off very fast if not properly lubricated, run at desired temperature and clean environment. Even if these are maintained, still many components are not designed to run for entire service life of the tractor. The life of lubrication oil used is increasing due to shifting to synthetic oils from petroleum based lubricating oils; still these are changed after 250 to 350 hours of engine operation. Slowly we are moving to manufacturing technologies and improvised alloys by adopting this short service (service at initial 50/100 hours of operation) is not required. Vehicle is just inspected for any loose nuts and bolts, clearances and deflections are checked and that is all done in short service or first service of tractor. However tractors manufactured with existing machine tools may require short service.
Essentially it is maintaining lubrication, desired temperature and clean environment inside the tractor engine and other housing besides maintaining proper clearances, tightness and deflection of components of tractor for achieving desired service life.
Clean environment inside the engine is achieved by maintaining intake system, i.e.
1) By cleaning pre cleaner periodically,
2) By maintaining correct level of right grade of oil in air cleaner and changing it as and when required
3) By cleaning the dry filter element periodically and changing it as and when required
4) By changing different filter elements at periodic service intervals.
Desired temperature can be maintained by maintaining cooling system. This is accomplished by keeping correct level of water or coolant in radiator or dispenser bowl, by keeping radiator or fins clean.
Desired level of lubrication is simply maintained by changing lubrication oils in different assemblies of tractor periodically along with filter elements.
Other required activities are to keep the tractor clean and dry after a day’s work, to tighten the loose nuts and bolts. By maintaining correct level of correct fluid in power steering system, brake housing, steering housing, battery and fuel injection pump etc. wherever required.
In short, tractors when put to use consume diesel, air and negligible quantity of
mobile oil. There is some degree of wear and tear of all working parts which can
be minimised with proper care and maintenance. Certain procedure has
been laid down for this, which if followed will produce best results on tractor performance. These services needs have been classified into hours ranging from ten to several hundred hours of tractor use.
These few very small activities can ensure that tractor runs for the designed service life. Service schedules generally maintain these conditions. Since, it is not necessary and possible also to carry out all above activities every hour. Activities required to be carried out at regular intervals to maintain these conditions are mentioned in service scheduled. Generally these are classified as 10, 50, 125, 250, 500, 1000 hour service schedule. The activities carried out in these schedules may vary marginally from one manufacturer to another for example ten hour service schedule list the activities to be carried out after a day’s work at Farm. The list of activities to be carried out in 10 hour service schedule has been listed below.
List of activities to be carried out in 10 hours service schedule:
-
Clean the tractor, if the tractor worked under dusty conditions & wash it with a swift jet of water to remove the dirt and wipe off with a dry cloth.
-
Inspect the tractor critically to ensure that no leakage is taking place at any point, take correct steps with the help of authorised service centre if the need be.
-
Check all the nuts and bolts for tightening properly on different parts of the tractor and replace the broken ones, if any.
-
Top up the fuel level in the fuel tank at the end of each days operation. This will keep your tractor ready for "next day and avoid condensation of water at the bottom of tank or in the fuel line.

Fig: 1. View of fuel tank (Courtesy: Sharma and Jain)
5. Check and top up, if necessary crank case with mobile oil. Dip stick with low and full level mark is provided for the purpose. The oil level should be in the middle of these two marks.
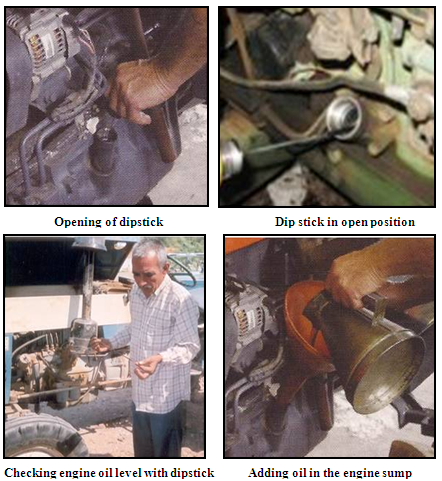
Fig: 2. View of checking and replenishing engine oil level (Courtesy: Tractor manual, Department of FPM, CCSHAU)
6.Clean pre cleaner. Check air cleaner oil level and if this level is less than the indicated mark or cut hole then top it.

Fig: 3. View of oil bath type air cleaner (Courtesy: Tractor manual Department of FPM, CCSHAU)
7. Check up the water/coolant level in the radiator/ dispenser bowl and top if necessary. Do not allow water level to go below from the top of the radiator.
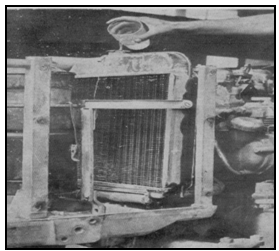
Fig: 4. View of Radiator and its filling (Courtesy: Tractor Manual, Department of FPM, CCSHAU)
8.Check the belt pulley gear-box oil level when the pulley is in use and refill it to the plug level with transmission oil.
9. Check the front and rear type-pressure. In general, the pressure in the front tyres should be nearly 2 kg/cm2 and that in the rear tyres about 1 kg/cm2".
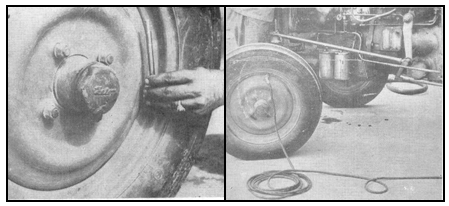
Fig: 5. View of tyre pressure checking of tractor (Courtesy: Tractor Manual, Department of FPM, CCSHAU)
Greasing of different points in tractor
References:
Sharma D N. & S. Mukesh (2004). Design of Agricultural Tractor (Principles and Problems) Book Pub. Jain Brothers, New Delhi
Wadhwa D.S., Dhingra H. S. & Santokh, Singh Field operation and maintenance of tractor and farm machinery (FMP-301), laboratory manual by, Department of Farm Machinery and Power Engineering, PAU Ludhiana
Sharma D N., Tractor Manual, Department of Farm Power and Machinery, CCSHAU