Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1. Introduction to by-products and waste ge...
Module 2. Waste management concepts
Module 3. Direct combustion of solid waste
Module 4. Thermo-chemical conversion of solid waste
Module 5. Bio-chemical conversion of solid waste
Module 6. Solid waste management
Module 7. Effluent treatment and disposal
Module 8. Presence of typical chemicals
19 April - 25 April
26 April - 2 May
Lesson 12.
BOD and COD are common measurements to determine water quality. They measure the strength of waste stream by measuring the O2 required to stabilize the wastes. As these substances degrade they consume dissolved O2 in water. The amount of O2 used is thus a good indicator of their amount of organic waste present. BOD and COD are important in food processing industry because they can be used to indicate lost products and wasteful practices. High BOD and COD levels indicate increased amounts of product lost to the waste streams. COD values are always greater than BOD values because of the nature of the measurement procedure. With the dichromate refluxing procedure used to measure COD almost all organic compounds are oxidized. However, with BOD procedure, some of these compounds do not fully oxidize making oxygen demand lower.
Characteristics of Food processing waste water
|
Parameters |
COD(mg/l) |
BOD(mg/l) |
|
Dairy |
900-7000 |
500-5000 |
|
Olive oil mill |
20400-77200 |
- |
|
Winery |
7130-27200 |
600-1400 |
|
Vegetables |
250-15000 |
125-4700 |
|
Cheese |
1000-7500 |
588-5000 |
|
Mixed dairy processing waste waters |
1150-9200 |
4700 |
|
Bakery products |
3200 |
7000 |
|
Jams and jellies |
2400 |
4000 |
|
Meat packing |
1433 |
2746 |
|
Meat specialities |
530 |
900 |
|
Poultry process |
1306 |
1581 |
|
whey |
32000 |
70000 |
The trickling filter
The trickling filters are also called percolating filters. The trickling filters are similar to contact beds in construction but allows constant aeration and the action is continues. The main function of the trickling filter is to remove unstable, organic materials in the form of dissolved and finely divided organic solids, and to oxidize these solids biologically to form more stable materials. In the trickling filter no sludge is returned to the incoming waste water. Rather the waste water is sprayed uniformly by a rotating distributor on a bed of rocks 6-10 ft deep. The rotation may be powered by an electric motor or a hydraulic impulse. The water percolates over the rocks within the bed which are 1-4 in diameter and is collected in an under-drain. The liquid is then collected from the under drain and allowed in a sedimentation tank which is an integral component of the trickling filter. The sludge from the sedimentation tank is removed from time to time. Various modifications of this basic system exist. In one modification the water may be pre-sedimented before introduction to the filter. Two filters may be placed in series and the effluent may be recycled. A coating of microorganisms form on the stones as the waste water trickles down the filter and these organisms break-down the waste. Fungi, algae, protozoa and bacteria form a thin film called zoogleal slims on the rocks. As the filter ages the aerobic bacteria which are responsible for the breakdown of the organic matter become impeded, the system becomes inefficient and flies and obnoxious smells may result. The microbial coating sloughs off from time to time. As the biota unable to cling to the film die, they are discharged from the filter with more or less partially decomposed organic matter. This is called ‘sloughing’. The sloughing of material may occur periodically as in a standard rate filter or continuously as in a high rate filter.
The essential features necessary to the process are:
Sufficient surface area must be provided for biological growth.
Free O must be available at the surface to replenish the dissolved O extracted from the liquid layer.
Industrial wastes must be amenable to biological treatment.
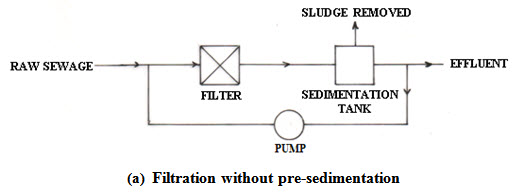
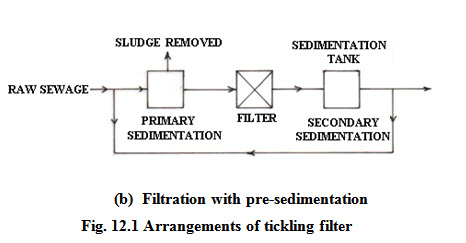
Advantages of trickling filters
They are self cleaning rate of filter loading is much higher.
No diminishing of capacity. Even if overdosed, they can recoup rest.
They are cheap and simple in operation.
Mechanical wear and tear is very small.
Disadvantages of trickling filter
High head loss through the filter making automatic dosing of filters as necessary.
Problem of odour and fly
Large land area is required. Cost of contraction is relatively higher.
They require preliminary treatment and therefore can not raw waste as such.
Rotating discs
Rotating discs are also known as rotating biological contractors. These consist of closely packed discs of PVC mounted on a horizontal shaft and patially (35-40%) submerged in waste water contained in a cylindrical tank made of steel or RCC. The discs are rotated slowly at 1-2 revolutions per minute by means of a driving mechanism. As the discs rotate out of water, aeration is achieved by exposure to atmosphere. As the waste water flows down through the discs, the submerged micro-organisms absorbs food and picks up a thin layer or 2 lime of waste water. With repeated action, a microbial film of 1-2 mm thickness develops. The disc rotation enables the slimy layer to slide down and mix with the substrate. This results in solids sloughing which is kept in suspension till its removal along with the effluent. The action is similar to the biological action taking in the trickling filter. Staging is the essential part of the RBC system. This requires compartmentalization of RBC discs to form a series of independent cells. Stages can be accomplished by using baffles in a single tank or by use of separate tank in series.
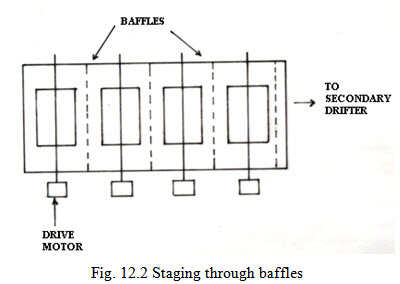
Advantages of RBC
Compared to the trickling filter, the hydraulic and organic loading rates are much less for primary settled sewage though BOD removal efficiency could be as high as 90% for a detention period of 1-2hrs.
Simplicity of operation
Relatively low energy cost