Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
MODULE 1. Systems concept
MODULE 2. Requirements for linear programming prob...
MODULE 3. Mathematical formulation of Linear progr...
MODULE 5. Simplex method, degeneracy and duality i...
MODULE 6. Artificial Variable techniques- Big M Me...
MODULE 7.
MODULE 8.
MODULE 9. Cost analysis
MODULE 10. Transporatation problems
MODULE 11. Assignment problems
MODULE 12. waiting line problems
MODULE 13. Network Scheduling by PERT / CPM
MODULE 14. Resource Analysis in Network Scheduling
LESSON 3. CRITICAL PATH METHOD
Time Calculations in Networks
For each activity an estimate must be made of time that will be spent in the actual accomplishment of that activity. Estimates may be expressed in hours, days, weeks or any other convenient unit of time. The time estimate is usually written in the network immediately above the arrow. The next step after making the time estimates is the calculation of earliest times and latest times for each mode. These calculations are done in the following way.
a) Let zero be the starting time for the project. Then for each activity there is an earliest starting time (ES) relative to the project starting time. The earliest finishing time is denoted by
Thus the formula is
EFi (or) ESj = max {ESi + tij}
Where Esj denotes the earliest start time of all the activities emanating from node i and tij is the estimated duration of the activity i-j.
Example:
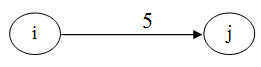
In the above example the activity is from i-j, the duration of time is 5 hours. Here start time is ESj= max {ESi + tij}
Initial start time ESi=0.
ESj= max {0+ 5} =5.
Initially the starting time will be 0 The finishing time for the ith event is 5.Staring time for the jth event is 5.
b) Let us suppose that we have a target time for completing the project. Then this time is called the latest finish time (LF) for the final activity. The latest start time (LS) is the latest time at which an activity can start if the target is to be maintained. It means that for the final activity, its LS is simply LF – activity time.
LFi = min {LFj – tij}, for all defined (i, j) activities.
Critical Path:
Certain activities in a network diagram of a project are called critical activities because delay in their execution will cause further delay in the project completion time. Thus, all activities having zero total float value are identified as critical activities.
The critical path is the continuous chain of critical activities in a network diagram. It is the longest path starting from first to the last event and is shown by a thick line or double lines in a network.
The length of the critical path is the sum of the individual times of all the critical activities lying on it and defines the minimum time required to complete the project.
The critical path on a network diagram can be identified as:
(a) ES i = LFi
(b) ES j = LFj
(c) ES j – ESi = LFj – LFi = tij.
Critical Path Method (CPM)
The iterative procedure of determining the critical path is as follows:
Step 1: List all the jobs and then draw a network diagram. Each job is indicated by an arrow with the direction of the arrow showing the sequence of jobs. The length of the arrows has no significance. Place the jobs on the diagram one by one keeping in mind what precedes and follows each job as well as what job can be done simultaneously.
Step 2: Consider the job’s times to be deterministic. Indicate them above the arrow representing the task.
Step 3: Calculate the earliest start time (EST) and earliest finish time (EFT) for each event and write them in the box marked ![]() Calculate the latest start time (LST) and latest finish time (LFT) and write them in the box marked
Calculate the latest start time (LST) and latest finish time (LFT) and write them in the box marked ![]() .
.
Step 4: Tabulate various times, i.e., activity normal times, earliest times and latest times, and mark EST and LFT on the arrow diagram.
Step 5: Determine the total float for each activity by taking differences between EST and LFT.
Step 6: Identify the critical activities and connect them with the beginning node and the ending node in the network diagram by double line arrows. This gives the critical path.
Step 7: Calculate the total project duration.
Slack / Float of an Activity and Event
The float (Slack) or free time is the length of time to which a non-critical activity and the time between its ES & LF is longer than its actual duration or an event can be delayed or extended without delaying the total project completion time.(ie) the difference between the latest finish and earliest start time.
There are four types of floats namely
a) Total float
b) Free float
c) Independent float
d) Interference float
a) Total float
Difference between the latest finish and earliest finish time for the activity
Total float = TFij = LFj - EFj
b) Free float
It is defined by assuming that all the activities start as early as possible. The free float for the activity (i, j) is the excess available time over its duration.
LFij = ESj – ESi - tij
c) Interference float
The difference between total float and free float.
d) Independent float
The time by which an activity can be rescheduled without affecting the preceding or the succeeding activities is known as independent float.
Independent float = Free float – Tail event Slack
Advantages of Critical Path Method(CPM)
-
CPM was developed for conventional projects like construction project which consists of well know routine tasks whose resource requirement and duration were known with certainty.
-
CPM is suited to establish a trade off for optimum balancing between schedule time and cost of the project.
-
CPM is used for projects involving well know activities of repetitive in nature.
However the distinction between PERT and CPM is mostly historical.
Problem
CPM
The following table gives the activities of a construction project and duration.
|
Activity |
1-2 |
1-3 |
2-3 |
2-4 |
3-4 |
4-5 |
|
Duration (days) |
20 |
25 |
10 |
12 |
6 |
10 |
(i) Draw the network for the project.
(ii) Find the critical path.
(iii) Find the total, free and independent floats each activity.
Solution:
The first step is to draw the network and fix early start and early finish schedule and then late start-late finish schedule as in figure 1 and figure 2.
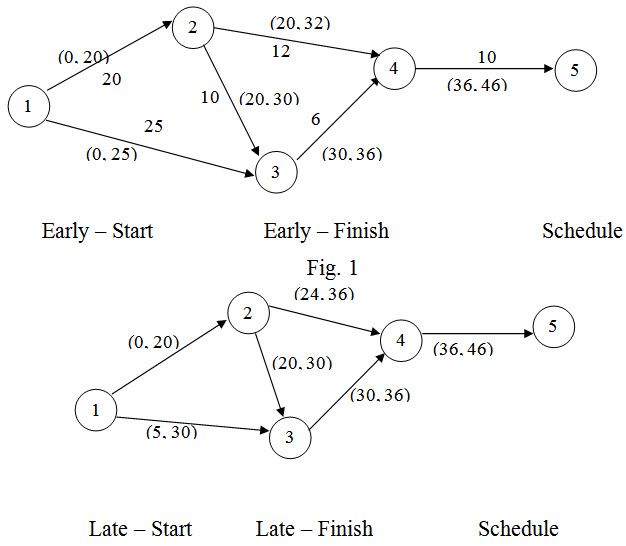 Fig.-2
Fig.-2
|
Activity |
Total Slack |
Free Slack |
Independent Slack |
|
1-2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
1-3 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
2-3 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
2-4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
|
3-4 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
4-5 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
To find the critical path, connect activities with ) total slack and we get 1-2-3-4-5 as the critical path.
Check with alternate paths.
1-2-4-5 = 42
1-2-3-4-5 = 46*
1-3-4-5 = 41