Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1. Moisture content and its determination.
Module 2. EMC
Module 3. Drying Theory and Mechanism of drying
Module 4. Air pressure within the grain bed, Shred...
Module 6. Study of different types of dryers- perf...
Module 5. Different methods of drying including pu...
Module 7. Study of drying and dehydration of agric...
Module 8. Types and causes of spoilage in storage.
Module 9. Storage of perishable products, function...
Module 10. Calculation of refrigeration load.
Module 11. Conditions for modified atmospheric sto...
Module 12. Storage of grains: destructive agents, ...
Module 13. Storage of cereal grains and their prod...
Module 14. Storage condition for various fruits an...
Module 15. Economics aspect of storage
Lession-34 Types of Grain storage structures
Grain is generally stored either in bags or in bulk. A combined system of bag-cum-bulk storage is also practiced in some parts of the country. In villages the bulk storage system is more common than the storage in bags which is considered to be a practicable method· of storing grain in the government godowns as well as in trade. There main following three types of storage structures for storage of grains.
-
Traditional storage structures
-
Improved storage structures
-
Modern storage structures
-
Farm Silos
34.1 Traditional Storage Structures
In this types of storage structures the grain is generally stored in bulk. This types of storage structures having generally capacities between 1 to 50 tonnes. The storage of grain is generally done in one of the following storage structures in the different rural and urban regions of India in bulk as well as in bag storage.
Morai type storage structures
Bukhari type storage structures
Kothar type storage structure
Mud Kothi type storage structure
Muda type storage structure
Kanaj type storage structure
Kuthla type storage structure
Metal/ Steel bin type storage structure
Bag type storage structure
34.2 Improved Storage Structures
Improved storage structures are the storage structures for storage of food grains. In this type of storage structures there are some improvements made in traditional storage structures. This type of storage structures having a higher storage capacity and long term storage of food grains than traditional storage structures. Improved type of storage structures having capacities is generally 1.5 to 150 tonnes. The storage of grain is generally done in one of the following storage structures in the different rural and urban regions of India in bulk, bag as well as bag and bulk storage.
34.2.1 Pusa bin
Pusa bin is like other traditional storage structures made of mud. To make the storage structure moisture proof a plastic film is used in all the inner sides of the bin.
34.2.2 Brick and cement bin
These type of storage structures are very strong and effect of seasons on these is minimum.
34.2.3 Bunker Storage
These type of storage structure is used for long term storage and a larger volume of grains storage.
34.2.4 'CAP' Storage structures
The word 'CAP' is used for cover and plinth, plinth from the bottom and cover from the top. This type of open storage is considered as transit storage and serves the purpose of storage of food grains in bags for short period.
34.3 Modern Storage Structures
In India, for larger volume of food grains are to be stored in bulk is 'silo' and conventional godowns (Shed) designed for bagged storage. The godowns side walls are of brick or stone masonry and sloped roofing in asbestos or Corrugated Galvanized Iron (CGI) sheets over steel trusses. Silos are constructed from steel or reinforced concrete. There are a cluster of adjoining silos in any modern large/ capacity processing plant. The modern permanent storage system should be selected for the safe keeping of stored grains and other products. The modern storage structures should be selected on the basis of first on quality and then on cost considerations. There are following types of modern storage structures.
34.3.1 Silo type of storage structures
Silos/bins are classified into two groups depending upon the relative dimensions of the container. These are classified as, (1) deep bins and (2) shallow bins.
34.3.1.1 Shallow bins
Squat silos are comes under shallow bins. A squat silo has a wall height to diameter ratio 0.5 or even less. Squat silo can compete with sheds for low-cost quality storage.
34.3.1.2 Deep bins
Vertical Silos are comes under this type of storage structures. There are two types of vertical silos a) Flat bottom vertical silo and b) Hopper bottom vertical silo.
34.3.2 Shed
Generally, a horizontal sheds have been used to provide low- cost, large volume storage. For storing grains and other products a very large volume sheds have also been constructed by Central Warehousing Corporation.
34.4 Farm Silos
Farm silos is a farm structure used to store and protect the animal fodder so that it is preserved in an ideal condition for farm animals. Animal fodder is cut and packed in the air tight silo to allow a partial fermentation to occur. The storage fodder is known as silage. There are two types of farm silos i) Tower silos and ii) Horizontal silos.
34.4.1 Tower silos
Cylindrical Shpe and made of masonary, wood or metal
Cost of construction is comparatively much higher than that of horizontal type.
Loading of animal fodder is difficult.
Mechanical loader or a large capacity of blower is essential.
This type of storage structures are not recommended under Indian conditions.
34.4.2 Horizontal silos
In horizontal silos pit type, bunker type and trench or stake type of storage structures used for storage of animal fodder.
There are surface as well as below ground (underground) types of storage structures used on most of dairy farms as temporary and permanent storage structures for silage.
The spoilage of silage and dry matter losses of these silos ranges between 20 to 30 percent.
34.4.2.1 Pit Silos
Permanent pit silo is a circular deep well which is lined all around the side, and sealed from bottom, so that water may not rise in to it.
Made in areas where the soil is deep and the water table is very low.
Made of bricks, stones or concrete, and either cement or lime can be used as a binding material.
A 22.5 cm thick wall will be used satisfactory up to 15 meter depth.
The entire surface which is coming in contact with the silage should be plastered to make it smooth, air tight and water tight.
Simple roof is made over the silo to protect the silage from sun and rain.
Corrugated metal sheet dome or half pitch roof with ample overhang on all the sides are most economical and provide more space for filling.
Stairs may be built along with wall for removing silage from the silo.
The diameter of a silo is usually limited to 6 m and its depth is kept 2 to 3 times that of diameter.
When the silo is opened for removing the silage, nobody should enter till the gases are removed.
34.4.2.2 Trench Silos
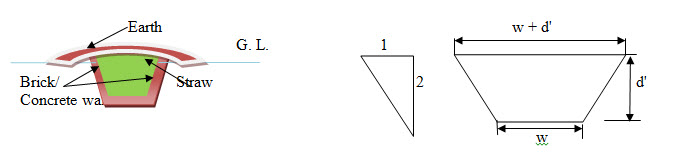
Fig. 34.1 Cross – section of trench silo showing wall lining
Unlined trench silo can be made easily without involving any investment on building materials such as brick, cement and sand.
Unlined silos give more spoilage and are likely to have caved side walls due to excessive rain and tend to become muddy at the bottom. So, lined trench silos are therefore become popular.
The walls of the trench silos can be lined with brick, concrete or cement plaster with reinforcing wire mesh.
If possible the silo should be roofed.
Drains should be made around trench to intercept surface water.
To facilitate drainage it is desirable to locate the trench silo on slopping ground.
Capacity is depends on size of herd and number of day the silage is fed in a year.
It is always economical to construct only one trench silo, even if it is quite larger.
Sidewalls are given generally 33 per cent slope.
References:
-
A Text Book Unit Operations of Agricultural Processing by K.M Sahay and K.K.Singh
-
Agriculture Engineering, Volume-I by A.M. Mickal and T.P.Oza
-
Sinha, R.N &Muir. Grain Storage: Part of a System. Avi Publisher.