Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1. Moisture content and its determination.
Module 2. EMC
Module 3. Drying Theory and Mechanism of drying
Module 4. Air pressure within the grain bed, Shred...
Module 6. Study of different types of dryers- perf...
Module 5. Different methods of drying including pu...
Module 7. Study of drying and dehydration of agric...
Module 8. Types and causes of spoilage in storage.
Module 9. Storage of perishable products, function...
Module 10. Calculation of refrigeration load.
Module 11. Conditions for modified atmospheric sto...
Module 12. Storage of grains: destructive agents, ...
Module 13. Storage of cereal grains and their prod...
Module 14. Storage condition for various fruits an...
Module 15. Economics aspect of storage
Lesson-35 Types of Traditional storage structures i.e., Bhukhari, Morai, Kothar
In this types of storage structures the grain is generally stored in bulk. This types of storage structures having generally capacities between 1 to 50 tonnes. The storage of grain is generally done in one of the following storage structures in the different rural and urban regions of India in bulk as well as in bag storage.
35.1 Morai type storage structure
Morai type of structure is used for the storage of paddy, maize and sorghum (jowar) in the rural areas of eastern and southern regions of India. Its capacity varies from 3·5 to 18 tonnes. These structures are very similar to the shape of an inverted cone. They are placed on a raised platform supported on wooden or masonry pillars. The improved type of structure consists of a circular wooden plank floor supported on pillars by means of timber joints. The planks are joined together with lap joints. All around the wooden floor a 22 gauge corrugated metal cylinder of 90 cm height is nailed to it. The edge of the cylinder is flushed with the bottom end of the floor. Inside the cylinder, 7·5 cm diameter ropes made of paddy straw or similar material are placed, beginning from the floor level upto a height of 90 cm. Then bamboo splits are placed vertically along the inner surface without leaving any gap between them. The height of the bamboo splits is equal to the total height of the structure. Keeping the bamboo splits in position, the grain is poured in up to the height of the metal cylinder. By then the bamboo splits are held erect in position. Now the winding of the rope as well as the pouring in of grain are done simultaneously. This process continues tiIl the required height is attained. The top most ring of the rope is secured in position by tying to the lower four rings. To provide a smooth surface, about 1 cm thick layer of mud plaster is applied over the rope. A conical roof is placed on the top of the structure having an ample overhang all around. (Fig. 35.1)
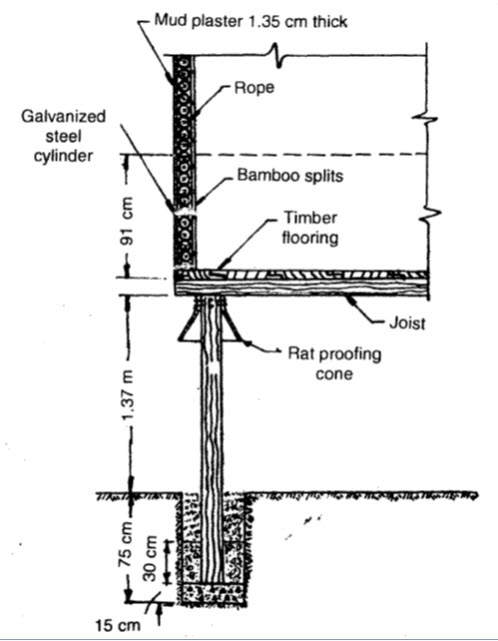
Fig.35.1 Morai type grain storage structure~vertical section
35.2 Bukhari type storage structure
Bukhari type storage structures are cylindrical in shape and are used for storage of sorghum, wheat, padd)" Bengalgram, maize etc. Bukhari structures generally have capacities between 3.5 to 18 tonnes, however, smaller capacity structures also exist. This may be made by mud alone or by mud and bamboo. The cylindrical storage structures are raised above the ground by wooden or masonry platform. The floor of the bin is made either by timber planks or by bamboo splits, plastered over with mud rilixed with dung and paddy straw. The walls of the structure are made of timber or bamboo frame work and bamboo matting. Over the walls, mud-straw plaster is applied on both sides. An overhanging cone type roof is provided on the cylindrical structure. The roof is generally made of bamboo framework and straw.
In improved bukhari type structure, the basic shape remains the same but the material and method of construction have been improved to make the structure more safe and durable. The circular floor of structure is either made of wooden planks joined by lap joints or by a double layer of bamboo splits closely set at right angles to each other. Over the floor, about 5 cm thick mud plastering is provided. The walls of structure are made of two sets of strong bamboo framework. The inter-space is filled with mud. The walls on both sides are plastered with mud. The roof is conical and made of bamboo frame-work and covered with paddy straw or similar other thatching material. The top of the conical roof is covered with 4 to 5 cm thick mud layer to provide additional protection from rains. The structure is raised on timber or masonry pillars to a height of about 1.5 m from ground level. Rat proofing cones are placed on all the four pillars to avoid rats entering the storage structure. (Fig.35.2)
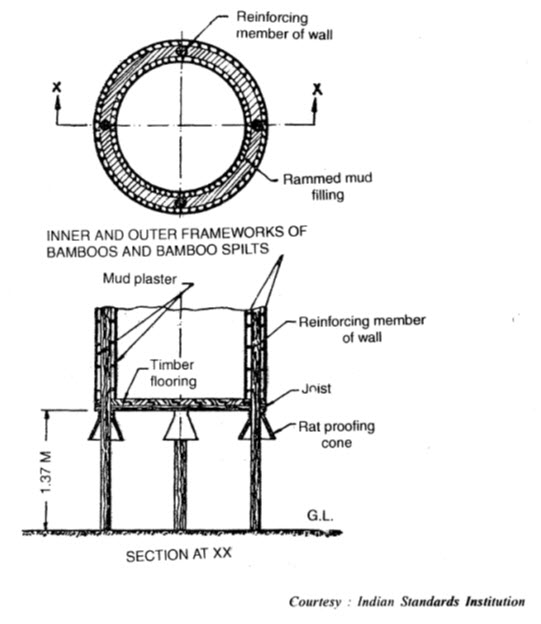
35.2 Bukhari type Grain Storage Structure - Vertical Section
35.3 Kothar type storage structure
These are used to store paddy, maize, sorghum, wheat etc. Their capacity varies between 9 to 35 tonnes. The storage structure is box like made of wood and raised on pillars. Both the floor and walls are made of wooden planks whereas the thatched or tiled roof is placed over it to protect the grains from the sun or rain. The improved Kothar structure is generally made of 5 cm thick wooden planks and beams. The walls and floor are made in such a way that no gap exists between the planks. The gabled roof on the top may be made of planks or corrugated metal sheets and should be sufficiently overhang on all sides. The storage structure is raised on timber post to a height of about 1.5 m above the ground. Rat proofing cones are provided on all posts to avoid entry of rats in the structure. (Fig.35.3)
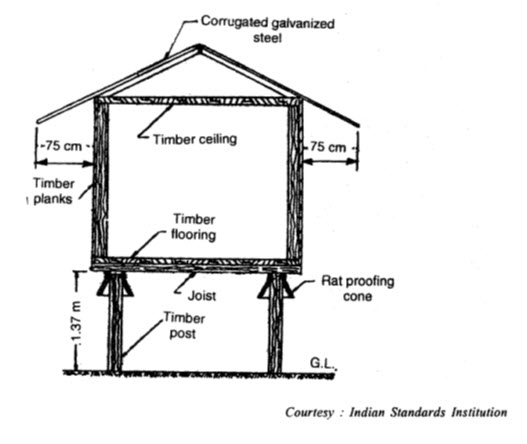
35.3 Kothar type Grain Storage Structure - Vertical Section
35.4 Mud Kothi (Mud bin)
These storage structures are quite common in rural areas for storage of grains and other seeds. The capacity of such storage structures varies from 1 to 50 tonnes. These are made from mud mixed with dung and straw. These Kothies are generally rectangular in shape but cylindrical Kothi is also common in some region. There are many sizes and dimensions of Kothi made for storing grains. (Fig.35.4)
35.5 Muda type of storage Structure
These are in use for storing grains in the rural areas of Bihar. The capacity of muda varies between 1 to 3 tonnes. It is being made of "Narai" ropes. The shape of muda is cylindrical and being made in various sizes.
35.6 Kanaj type of Storage Structure
These storage structures are very common in the rural areas of Karnataka and Maharashtra for storage of grains. The capacity of Kanaj varies between 1 to 20 tonnes. It is being made by bamboo splits. The shape of storage structure is cylindrical. The walls of storage structure are sealed with mud plaster on both sides. The roof of the structure is conical and thatched. The roof overhang on all sides.
35.7 Kuthla
These storage structures are very much common in rural areas of Bihar and Uttar Pradesh. These structures are kept inside and made of burnt mud.
35.8 Bag Storage Structure
These structures are generally used for the storage of 25 to 500 tonnes of grain. The length of the structure is about twice the width or greater than that. A typical floor plan of such a structure large enough to store about 6000 bags (500 tonnes) of grain. Bags of different capacities (35, 50, 75 and 100 kg) with or without inside plastic lining are used. The standard size of a 100 kg bag is 100 cm x 60 cm x 30 cm i.e. length of bag is 100 cm, width of bag is 60 cm and height of filled bag is 30 cm. This bag can store 93 Kg of Wheat and 75 Kg of Paddy.

35.5 Different size of Bags for storage
35.9 Metal Bin
Bins made of steel, Aluminium R.C.C are used for storage of grains inside and outside the house. These bins are fire and moisture proof. The bins have long durability and produced on commercial scale. The capacity ranges from 50 kg to 10 tonnes.
References:
-
A Text Book Unit Operations of Agricultural Processing by K.M Sahay and K.K.Singh
-
Agriculture Engineering, Volume-I by A.M. Mickal and T.P.Oza
-
Sinha, R.N &Muir. Grain Storage: Part of a System. Avi Publisher.