Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1. Moisture content and its determination.
Module 2. EMC
Module 3. Drying Theory and Mechanism of drying
Module 4. Air pressure within the grain bed, Shred...
Module 6. Study of different types of dryers- perf...
Module 5. Different methods of drying including pu...
Module 7. Study of drying and dehydration of agric...
Module 8. Types and causes of spoilage in storage.
Module 9. Storage of perishable products, function...
Module 10. Calculation of refrigeration load.
Module 11. Conditions for modified atmospheric sto...
Module 12. Storage of grains: destructive agents, ...
Module 13. Storage of cereal grains and their prod...
Module 14. Storage condition for various fruits an...
Module 15. Economics aspect of storage
Lesson-36 Types of improved storage structures
In improved type of storage structures, there are some improvements made in traditional storage structures. These types of storage structures have a higher storage capacity for long term storage of food grains than traditional storage structures. Improved types of storage structures have capacities generally in the range of 1.5 to 150 tons. The storage of grain is generally done in one of the following storage structures in the different rural and urban regions of India.
36.1 Pusa bin
Pusa bin is just like other traditional storage structure and is made of mud. To make this storage structure moisture proof, a plastic film is used on inner side of the bin. A platform of mud bricks is made, first. On this platform, a sheet of 700 gauge plastic is spread in such a way that it overlaps the platform on all sides by atleast 6 cm. On the plastic sheet, a layer of 7 cm thick kachcha bricks is then laid. Walls are made of kachcha bricks and these are sealed with mud plaster. Now the walls are raised to proper height and a wooden frame is placed on it. The upper roof of the structure is made of burnt bricks. For unloading of grains, an inclined wooden or steel pipe is fixed in such a way that grains may come out of structure by gravity. The mouth of pipe is closed by a cover. The inside of all the four walls and roof are covered with a plastic sheet. On the top, an open space of about 50 cm x 50 cm is left for loading of grains. Leaving this open space, the roof is sealed by mud. After the bin is filled with grains, the top open space is well covered by a plastic sheet so that air may not enter the bin. A typical Pusa bin is shown in fig.36.1 below.
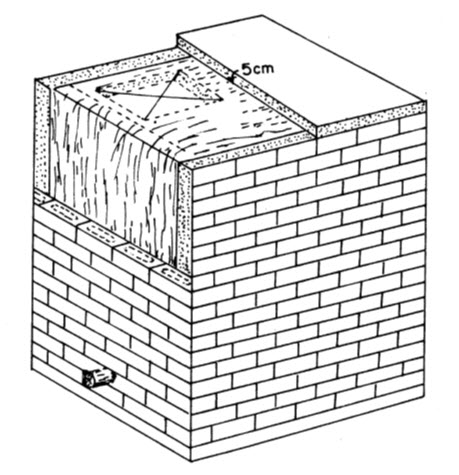
36.2 Brick and cement bin
These storage structures are very strong and therefore, the effect of season on them is negligible. The bin is made on a platform raised at 60 cm above the ground. A ladder is provided on one side of the bin for loading of the grains. A hole of about 60 cm diameter is provided on the roof for the purpose of loading the material i.e. grains. The walls of bin are about 23 cm thick with cement plastered on both the sides. Roof is made of R.C.C. The base of bin is made inclined and an outlet is provided for unloading of grains. The capacity of such bin is usually between 1.5 to 60 tonnes. For cleaning of bin and complete unloading, a provision of iron rings steps is provided inside the bin for person can enter and exit the bin.
36.3 Bunker Storage
Bunker storage structure is used for long term storage of a larger volume of grains. The structure is successful as a means of storing grains safely, securely and economically. By controlling insects and the moisture, the losses in stored grains can be reduced upto 0.5%. In this type of storage structure, the grain is stored on a plastic sheet which is spread over ground and top covered with plastic sheet as is shown in fig. 36.2. A drain is also provided for drainage of rain water.
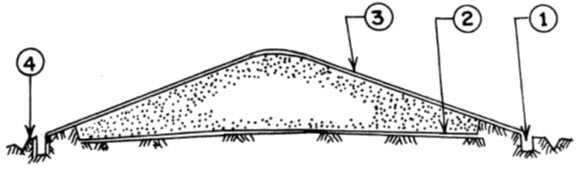
36.4 'CAP' Storage structures
The 'CAP' is used for cover and plinth storage. The word plinth is means plinth from the bottom and cover means cover from the top. This type of open storage is considered as intermediate storage and serves the purpose of storage of food grains in bags for short period. This type of storage facility is cheaper as compared to conventional bag storage godowns. The cover is rectangular in shape having five sides and made from polyethylene film of 1000 gauge, leaving the bottom side open. The cover is used for protecting stack of bags. Normally the stack is built over a space of 9.11 x 6.1 m with a height of 18 bags which gives the storage capacity of around 150 tonnes. The cover having a dimension of 9.4 m x 6.4 m x 5.5 m normally weighs around 52 kg. Sometimes smaller covers are used for covering the stacks in covered varandah of conventional godowns. Such covers are called "Varandah covers". For storage of food grains under varandah covers, the stacks are built to a height up to 7 bags having an average capacity of 24 tonnes.
The following steps are normally followed in the construction of a 'CAP' storage
(i) Select a high elevated ground and make it level.
(ii) Wooden sleepers are spread with one or two layers of bamboo mat cover on the top as
dunnage.
(iii) The Gutters are provided all around the area to drain off rain water easily.
(iv) The stacking is done to the height upto 18 bags on the dunnage and is covered with
polyethylene.
(v) The stacks arc covered with polyethylene covers and tied with ropes to prevent from blowing
off with high velocity wind.
References:
-
A Text Book Unit Operations of Agricultural Processing by K.M Sahay and K.K.Singh
-
Sinha, R.N & Muir. Grain Storage: Part of a System. Avi Publisher.