Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1. Introduction to Theory of Machine
Module 2. Planar Mechanism
Module 3. Velocity and Acceleration Analysis
15 March - 21 March
22 March - 28 March
29 March - 4 April
5 April - 11 April
12 April - 18 April
19 April - 25 April
26 April - 2 May
Lesson 23.
23.1 TYPES OF FLAT BELT DRIVES
Flat belt drives may be of any of the following types:
1) Open belt drives
In this type of arrangement the shafts are parallel to each other and rotate in the same direction as shown in the fig 5.2. The lower side belt also known as tight belt side has more tension than the upper side belt known as slack side. The driver pulls the belt from one side and delivers it to other side known as slack side.
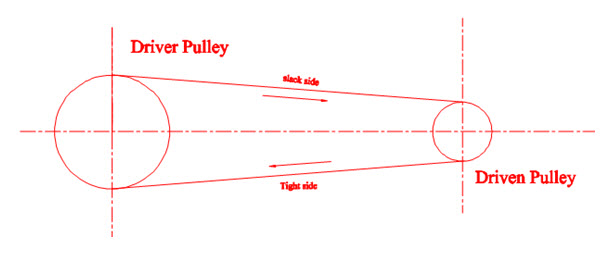
Fig 5.2 open belt drive
2) Crossed or twist belt drives
The arrangement of crossed belt drives is shown in the figure 5.3. Here the shafts are arranged in parallel. The belts rub against each other which cause wear and tear. There is driver pulley and driven pulley in the arrangement and they rotate in opposite direction.
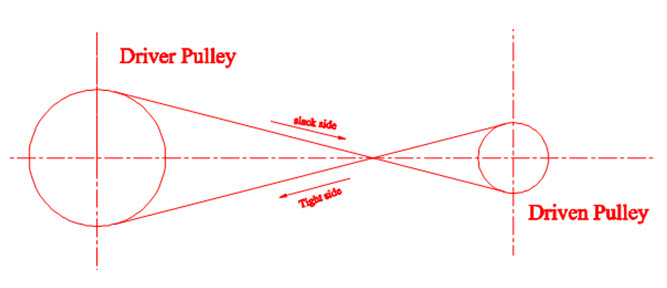
Fig 5.3 cross belt drive
3) Quarter turn belt drives
In this type of arrangement the shafts are arranged at right angles. The arrangement of the same is shown in the figure 5.4
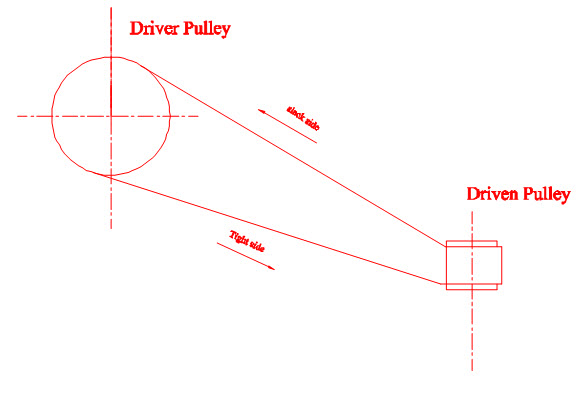
Fig 5.4 Quarter turn belt drive
4) Compound belt drives
Compound belt drives are used where power has to be transmitted through number of pulleys. The schematic diagram is as shown in the figure 5.5
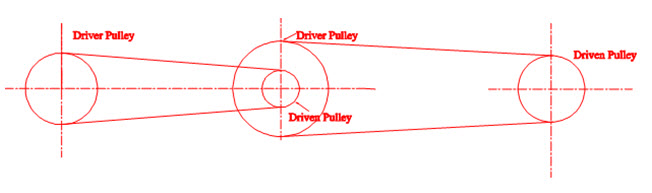
Fig 5.5 Compound belt drive
5) Stepped or cone belt drives:
Such belt drives are commonly used for changing the speed of driven shaft. The construction details for the same is shown in the figure 7.6
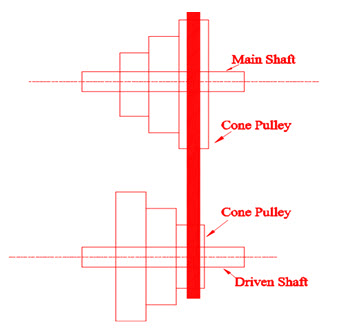
Fig 5.6 stepped or cone belt drive