Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
Module 1. Basic Concepts, Conductive Heat Transfer...
Module 2. Convection
Module 3. Radiation
Module 4. Heat Exchangers
Module 5. Mass Transfer
Lesson 7. Numericals on conduction
Thermal Insulation
The purpose of use of thermal insulation is to prevent or reduce transfer of thermal energy between two systems maintained at different temperatures. Thermal insulation is generally used in following applications
Protective clothing for human comfort
Design of energy efficient buildings
Air Conditioning systems
Refrigeration and food preservation
Automobiles
Boilers and steam pipes
Spacecraft
Value of thermal conductivity of a material is generally used as a measure of its insulating capabilities. Materials having lower value of thermal conductivity are considered to be insulators. Insulating capability of a material depends upon following factors
Thermal conductivity
Temperature
Density or Porosity
Specific heat
Surface emissivity
Moisture Content
Air Pressure
Convection with in insulating material
According to ‘Thermal Insulation Association of Canada’ thermal insulation is used for temperature range of -75 oC and 815 oC as for temperature range below -75 oC and higher than 815 oC, cryogenic and refractory materials are used respectively. Depending upon temperature range for which thermal insulation is to be used, insulating materials are categorized as
i) Low temperature insulating materials for temperature range of -75 oC to 15 oC
ii) Medium temperature insulating materials for temperature range of 15 oC to 315 oC
iii) High temperature insulting materials for temperature range of 315 oC to 815 oC
The most commonly used insulating materials and their properties are given in Table 1
TABLE 1– Thermal Conductivities of Insulating Materials (Powders)
|
|
Material |
Mean Temperature °C |
Conductivity (K) k cal/ m-hr-°C |
|
1. |
Alumina compressed powder |
50 |
7.0 |
|
2. |
Ashes, Soft wood |
25 |
0.33 |
|
3. |
Carbon black |
55 |
0.22 |
|
4. |
Coal dust |
40 100 |
1.20 1.32 |
|
5. |
Coke dust |
25 |
1.50 |
|
6. |
Charcoal |
15 |
0.54 |
|
7. |
Cork-granulated |
0 |
0 45 |
|
8. |
Floto foam |
35 |
0.30 |
|
9. |
Graphite powder |
40 |
1.40 |
|
10. |
Plaster of Paris |
25 |
10.5 |
|
11. |
Fine river sand Moistured |
10 |
3.3 |
|
12. |
Saw dust |
25 |
11.6 |
|
13. |
Silica |
30 |
0.06 |
|
14. |
Silica Aerogel |
315 480 650 |
0.80 0.84 0.93 |
|
15. |
Silica gel |
-70 -20 40 100 150 55 |
0.174 0.207 0.240 0.276 0.318 0.90 |
|
16. |
Snow |
0 |
0.51 to 1.9 |
Critical Thickness of Insulation
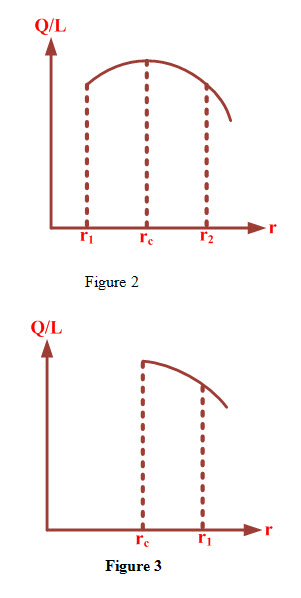
Addition of layer insulation to walls and slabs always reduces the heat transfer, however, in case of systems having cylindrical and spherical surfaces, addition of insulation does not reduce the heat transfer, rather it increases heat transfer rate upto certain thickness of insulation. As insulation layer is added to a bare pipe, heat transfer rate increases instead of decreasing. With further addition insulation layer, heat transfer rate goes on increasing till it attains a maximum value beyond which it decreases with increase in thickness of insulation material. The thickness of insulation corresponding to maximum heat transfer rate from the pipe is called critical thickness of insulation.
This concept of critical thickness of insulation finds a useful application in electric transmission cables. Transmission losses increase with increase in temperature as electric current passes through the cables. In order to reduce the transmission losses, it becomes imperative to increase heat transfer rate from cables to surroundings so that temperature of cables is reduced. This is achieved by keeping the thickness of insulation equal to its critical thickness.
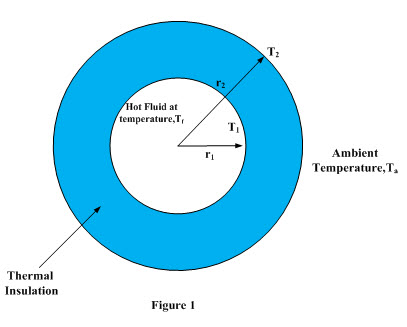
In order to determine the critical thickness of insulation, consider a cylinder of negligible thickness, length ‘L’, radius ‘r1’ carrying hot fluid of temperature T1. Temperature of hot fluid is higher than that of ambient temperature Ta. The cylinder is insulated by an insulating material having thickness‘t’ and thermal conductivity ‘k’. Thickness of insulation can be expressed as
t = r2 – r1 (1)
where r2 is the outer radius of the arrangement consisting of thin cylinder and layer of insulating material and it depends upon value of the thickness of insulating material. The arrangement has been shown in Figure 1.
Heat transfer rate per unit length from cylinder is expressed as
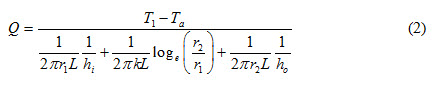
hi and ho inside and outside heat transfer coefficients of convection
By using equation (1), heat transfer rate per unit length can be determined for different value of r2. Total thermal resistance of the arrangement is sum of inside convective thermal resistance, conductive thermal resistance of insulating material and outside convective thermal resistance. Total thermal resistance of the arrangement depends upon the value of r2 which in turn depends upon the thickness of insulating material. As the thickness of insulation increase, r2 also increase resulting in increase in conductive thermal resistance and decrease in outer convective resistance. Therefore, increase in thickness of insulation will either result in increase or decrease in heat transfer rate depending on the overall change in the total thermal resistance.
For heat transfer rate per unit length to be maximum, thermal resistance should be the minimum. The value of r2, for which heat transfer rate per unit length will be maximum, can be obtained by differentiating total thermal resistance i.e. denominator of equation (2) with respect to r2 and equating equal to zero.
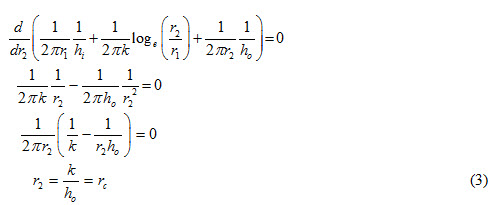
Equation (3) gives the value of thickness of insulation for which heat transfer rate per unit length is the maximum as corresponding total thermal resistance is the minimum. The value of thickness of insulation at which total thermal resistance is minimum is called critical thickness of insulation and is represented by rc and depends upon thermal conductivity and convective heat transfer coefficient of insulating material. Addition of insulation to a bare surface will either increase or decrease the heat transfer rate per unit lenth depending upon the value of critical radius and radius of bare surface.
i) If r1 < rc , the rate of heat transfer per unit length of cylinder increases as thickness of insulation increases. The heat transfer rate goes on increasing with increase in thickness of insulation and attains a maximum value corresponding to that value of insulation of thickness for which r2 becomes equal to rc as shown in Figure 2 . It is due to the fact that in ranger r1 less than rc, progressive decreases in convective resistance with increase in insulation thickness dominates over the corresponding increase in conductive resistance. The net effect is decreases in total thermal resistance and heat transfer rate per unit length increases.
ii) For the range r1 greater rc, heat transfer rate goes on decreasing with increase in insulation thickness as shown in Figure 3. It is attributed to the fact that in range r1 greater than rc, effect of conductive resistance dominates over that of the convective resistance resulting in increases in total thermal resistance. Therefore, heat transfer rate per unit length decreases.