Site pages
Current course
Participants
General
MODULE 1. Analysis of Statically Determinate Beams
MODULE 2. Analysis of Statically Indeterminate Beams
MODULE 3. Columns and Struts
MODULE 4. Riveted and Welded Connections
MODULE 5. Stability Analysis of Gravity Dams
Keywords
LESSON 17. Displacement Method: Moment Distribution Method – 3
17.1 Introduction: In this lesson the application of the Moment Distribution Method in continusous beam is illustrated via two examples.
Example 1
Draw the bending moment diagram for the following continuous beam. All spans have constant EI.
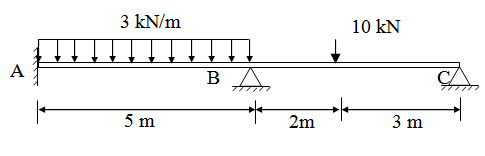 Fig. 17.1.
Fig. 17.1.
From lesson 15.1.3 we have,
\[{k_{BA}} = {{4E{I_{BA}}} \over {{L_{BA}}}} = {{4EI} \over 5}\] and \[{k_{BC}} = {{3E{I_{BC}}} \over {{L_{BC}}}} = {{3EI} \over 5}\]
Distribution factors for BA and BC are,
\[D{F_{BA}} = {4 \over 7}\] and \[D{F_{BC}} = {3 \over 7}\]
End A is fixed and therefore no moment will be carrid over to B from A. Carry over factors for other joints,
\[{C_{BA}} = {1 \over 2}\] , \[{C_{BC}} = {1 \over 2}\] , \[{C_{CB}} = {1 \over 2}\]
Fixed end moments are,
\[M{}_{FAB}=-{{3 \times {5^2}} \over {12}}=-6.25{\rm{ kNm}}\] ; \[M{}_{FBA} = {{3 \times {5^2}} \over {12}} = 6.25{\rm{ kNm}}\]
\[M{}_{FBC}=-{{10 \times 2 \times {3^2}} \over {{5^2}}}=-7.2{\rm{ kNm}}\] ; \[M{}_{FCB} = {{10 \times 3 \times {2^2}} \over {{5^2}}} = 4.8{\rm{ kNm}}\]
Calculations are performed in the following table.
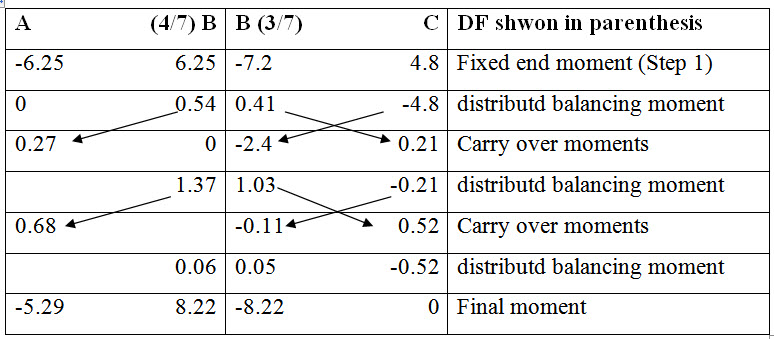
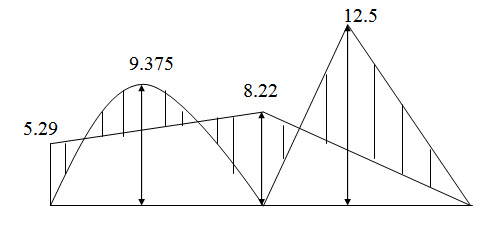 Fig. 17.2: Bending moment diagram (in kNm).
Fig. 17.2: Bending moment diagram (in kNm).
Example 2
Replace the fixed support at A by a hinge in the continuous beam shown in Example 1 and determine the bending moments.
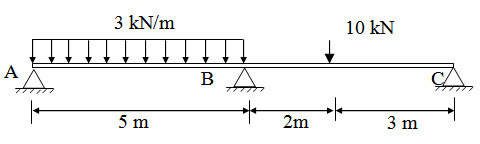
Fig. 17.3 .
From lesson 15.1.3 we have,
\[{k_{BA}} = {{4E{I_{BA}}} \over {{L_{BA}}}} = {{4EI} \over 5}\] and \[{k_{BC}} = {{3E{I_{BC}}} \over {{L_{BC}}}} = {{3EI} \over 5}\]
Distribution factors for BA and BC are,
\[D{F_{BA}} = {4 \over 7}\] and \[D{F_{BA}} = {3 \over 7}\]
Carry over factors,
\[{C_{AB}} = {1 \over 2}\] , \[{C_{BA}} = {1 \over 2}\] , \[{C_{BC}} = {1 \over 2}\] , \[{C_{CB}} = {1 \over 2}\]
Fixed end moments are,
\[M{}_{FAB}=-{{3 \times {5^2}} \over {12}}=-6.25{\rm{ kNm}}\] ; \[M{}_{FBA} = {{3 \times {5^2}} \over {12}} = 6.25{\rm{ kNm}}\]
\[M{}_{FBC}=-{{10 \times 2 \times {3^2}} \over {{5^2}}}=-7.2{\rm{ kNm}}\] ; \[M{}_{FCB}=-{{10 \times 3 \times {2^2}} \over {{5^2}}} = 4.8{\rm{ kNm}}\]
Calculations are performed in the following table.
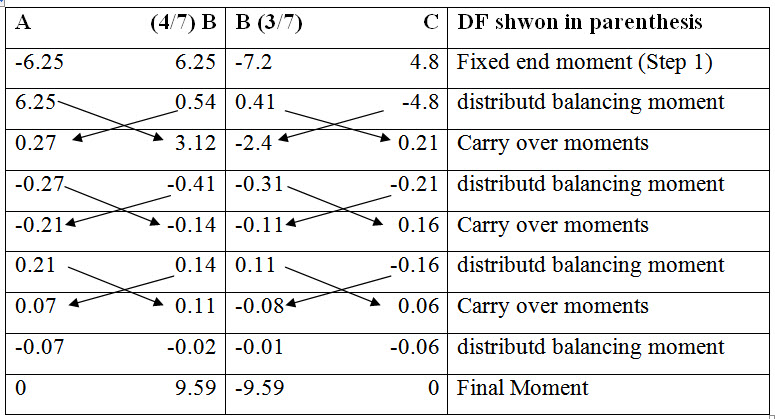
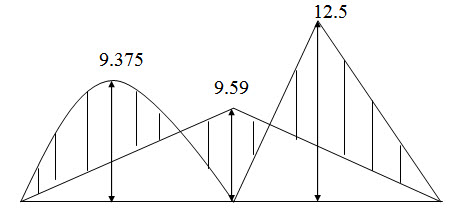
Fig. 17.4. Bending moment diagram (in kNm).
Suggested Readings
Hbbeler, R. C. (2002). Structural Analysis, Pearson Education (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.,Delhi.
Jain, A.K., Punmia, B.C., Jain, A.K., (2004). Theory of Structures. Twelfth Edition, Laxmi Publications.
Menon, D., (2008), Structural Analysis, Narosa Publishing House Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi.
Hsieh, Y.Y., (1987), Elementry Theory of Structures , Third Ddition, Prentrice Hall.